MicroRNA-221/222 negatively regulates estrogen receptor alpha and is associated with tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer
- PMID: 18790736
- PMCID: PMC2576549
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M806041200
MicroRNA-221/222 negatively regulates estrogen receptor alpha and is associated with tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer
Retraction in
-
MicroRNA-221/222 negatively regulates estrogen receptor α and is associated with tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer.J Biol Chem. 2016 Oct 21;291(43):22859. doi: 10.1074/jbc.A116.806041. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27825097 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
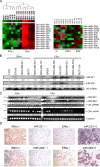
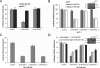
A search for regulators of estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) expression has yielded a set of microRNAs (miRNAs) for which expression is specifically elevated in ERalpha-negative breast cancer. Here we show distinct expression of a panel of miRNAs between ERalpha-positive and ERalpha-negative breast cancer cell lines and primary tumors. Of the elevated miRNAs in ERalpha-negative cells, miR-221 and miR-222 directly interact with the 3'-untranslated region of ERalpha. Ectopic expression of miR-221 and miR-222 in MCF-7 and T47D cells resulted in a decrease in expression of ERalpha protein but not mRNA, whereas knockdown of miR-221 and miR-222 partially restored ERalpha in ERalpha protein-negative/mRNA-positive cells. Notably, miR-221- and/or miR-222-transfected MCF-7 and T47D cells became resistant to tamoxifen compared with vector-treated cells. Furthermore, knockdown of miR-221 and/or miR-222 sensitized MDA-MB-468 cells to tamoxifen-induced cell growth arrest and apoptosis. These findings indicate that miR-221 and miR-222 play a significant role in the regulation of ERalpha expression at the protein level and could be potential targets for restoring ERalpha expression and responding to antiestrogen therapy in a subset of breast cancers.
Figures


References
-
- Giacinti, L., Claudio, P. P., Lopez, M., and Giordano, A. (2006) Oncologist 11 1-8 - PubMed
-
- Lee, R. C., Feinbaum, R. L., and Ambros, V. (1993) Cell 75 843-854 - PubMed
-
- Pasquinelli, A. E., Reinhart, B. J., Slack, F., Martindale, M. Q., Kuroda, M. I., Maller, B., Hayward, D. C., Ball, E. E., Degnan, B., Muller, P., Spring, J., Srinivasan, A., Fishman, M., Finnerty, J., Corbo, J., Levine, M., Leahy, P., Davidson, E., and Ruvkun, G. (2000) Nature 408 86-89 - PubMed
-
- Reinhart, B. J., Slack, F. J., Basson, M., Pasquinelli, A. E., Bettinger, J. C., Rougvie, A. E., Horvitz, H. R., and Ruvkun, G. (2000) Nature 403 901-906 - PubMed
-
- Ambros, V. (2001) Cell 107 823-826 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

