Curcumin inhibits Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling through protein phosphatase-dependent mechanism
- PMID: 18790744
- PMCID: PMC2596943
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-2400
Curcumin inhibits Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling through protein phosphatase-dependent mechanism
Abstract
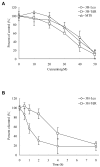
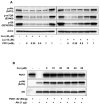
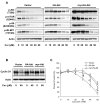
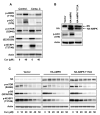
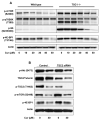
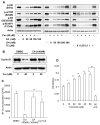
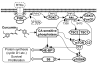
Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling plays an important role in tumorigenesis and is dysregulated in many tumors, especially metastatic prostate cancers. Curcumin has been shown to effectively prevent or inhibit prostate cancer in vivo and inhibit Akt/mTOR signaling in vitro, but the mechanism(s) remains unclear. Here, we show that curcumin concentration- and time-dependently inhibited the phosphorylation of Akt, mTOR, and their downstream substrates in human prostate cancer PC-3 cells, and this inhibitory effect acts downstream of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and phosphatidylinositol-dependent kinase 1. Overexpression of constitutively activated Akt or disruption of TSC1-TSC2 complex by small interfering RNA or gene knockout only partially restored curcumin-mediated inhibition of mTOR and downstream signaling, indicating that they are not the primary effectors of curcumin-mediated inhibition of Akt/mTOR signaling. Curcumin also activated 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinases; however, inhibition of these kinases failed to rescue the inhibition by curcumin. Finally, it was shown that the inhibition of Akt/mTOR signaling by curcumin is resulted from calyculin A-sensitive protein phosphatase-dependent dephosphorylation. Our study reveals the profound effects of curcumin on the Akt/mTOR signaling network in PC-3 cells and provides new mechanisms for the anticancer effects of curcumin.
Figures


References
-
- Hennessy BT, Smith DL, Ram PT, Lu Y, Mills GB. Exploiting the PI3K/AKT pathway for cancer drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4:988–1004. - PubMed
-
- Sarbassov DD, Guertin DA, Ali SM, Sabatini DM. Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the rictor-mTOR complex. Science. 2005;307:1098–101. - PubMed
-
- Belham C, Wu S, Avruch J. Intracellular signalling: PDK1--a kinase at the hub of things. Curr Biol. 1999;9:R93–6. - PubMed
-
- Toker A, Yoeli-Lerner M. Akt signaling and cancer: surviving but not moving on. Cancer Res. 2006;66:3963–6. - PubMed
-
- Cully M, You H, Levine AJ, Mak TW. Beyond PTEN mutations: the PI3K pathway as an integrator of multiple inputs during tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:184–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

