Chloroplast signaling and LESION SIMULATING DISEASE1 regulate crosstalk between light acclimation and immunity in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 18790826
- PMCID: PMC2570729
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.108.059618
Chloroplast signaling and LESION SIMULATING DISEASE1 regulate crosstalk between light acclimation and immunity in Arabidopsis
Erratum in
- Plant Cell. 2008 Dec;20(12):3480. Mateo, Alfonso [added]
Abstract
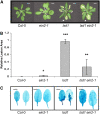
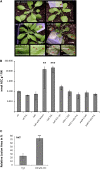
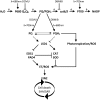
Plants are simultaneously exposed to abiotic and biotic hazards. Here, we show that local and systemic acclimation in Arabidopsis thaliana leaves in response to excess excitation energy (EEE) is associated with cell death and is regulated by specific redox changes of the plastoquinone (PQ) pool. These redox changes cause a rapid decrease of stomatal conductance, global induction of ASCORBATE PEROXIDASE2 and PATHOGEN RESISTANCE1, and increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ethylene that signals through ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE2 (EIN2). We provide evidence that multiple hormonal/ROS signaling pathways regulate the plant's response to EEE and that EEE stimulates systemic acquired resistance and basal defenses to virulent biotrophic bacteria. In the Arabidopsis LESION SIMULATING DISEASE1 (lsd1) null mutant that is deregulated for EEE acclimation responses, propagation of EEE-induced programmed cell death depends on the plant defense regulators ENHANCED DISEASE SUSCEPTIBILITY1 (EDS1) and PHYTOALEXIN DEFICIENT4 (PAD4). We find that EDS1 and PAD4 operate upstream of ethylene and ROS production in the EEE response. The data suggest that the balanced activities of LSD1, EDS1, PAD4, and EIN2 regulate signaling of programmed cell death, light acclimation, and holistic defense responses that are initiated, at least in part, by redox changes of the PQ pool.
Figures


References
-
- Asada, K. (1999). The water-water cycle in chloroplasts: Scavenging of active oxygens and dissipation of excess photons. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 50 601–639. - PubMed
-
- Ball, L., Accotto, G.-P., Bechtold, U., Creissen, G., Funck, D., Jimenez, A., Kular, B., Leyland, N., Mejia-Carranza, J., Reynolds, H., Karpiński, S., and Mullineaux, P.M. (2004). Evidence for a direct link between glutathione biosynthesis and stress defense gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16 2448–2462. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bartsch, M., Gobbato, E., Bednarek, P., Debey, S., Schultze, J.L., Bautor, J., and Parker, J.E. (2006). Salicylic acid-independent ENHANCED DISEASE SUSCEPTIBILITY1 signaling in Arabidopsis immunity and cell death is regulated by the monooxygenase FMO1 and the nudix hydrolase NUDT7. Plant Cell 18 1038–1051. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bechtold, U., Karpiński, S., and Mullineaux, P.M. (2005). The influence of the light environment and photosynthesis on oxidative signaling responses in plant-biotrophic pathogen interactions. Plant Cell Environ. 28 1046–1055.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

