Dissection of two Cx37-independent conducted vasodilator mechanisms by deletion of Cx40: electrotonic versus regenerative conduction
- PMID: 18790841
- PMCID: PMC2614564
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00063.2008
Dissection of two Cx37-independent conducted vasodilator mechanisms by deletion of Cx40: electrotonic versus regenerative conduction
Abstract
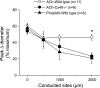
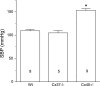
Conduction of changes in diameter plays an important role in the coordination of peripheral vascular resistance and, thereby, in the control of arterial blood pressure. It is thought that conduction of vasomotor signals relies on the electrotonic spread of changes in membrane potential from a site of stimulation through gap junctions connecting the cells of the vessel wall. To explore this idea, we stimulated a short segment of mouse cremasteric arterioles with an application, via micropipette, of ACh, an endothelium-dependent vasodilator, or pinacidil, an ATP-sensitive K+ channel opener. Vasodilations were evaluated at the stimulation site (local) and at 500, 1,000, and 2,000 microm upstream. The vasodilator response evoked by direct arteriolar hyperpolarization induced by pinacidil decayed rapidly with distance, as expected for the passive spread of an electrical signal. Deletion of the gap junction proteins connexin37 or connexin40 did not alter the conduction of pinacidil-induced vasodilation. In contrast to pinacidil, the vasodilator response activated by ACh spread along the entire vessel without decrement. Although the ACh-induced conducted vasodilation was similar in wild-type and connexin37 knockout mice, deletion of connexin40 converted the nondecremental conducted response activated by ACh into one similar to that of pinacidil, with a decline in magnitude along the vessel length. These results suggest that ACh activates a mechanism of regenerative conduction of vasodilator responses. Connexin40 is essential for the ACh-activated regenerative vasodilator mechanism. However, neither connexin40 nor connexin37 is indispensable for the electrotonic spread of hyperpolarizing signals.
Figures


References
-
- Bartlett IS, Segal SS. Resolution of smooth muscle and endothelial pathways for conduction along hamster cheek pouch arterioles. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 278: H604–H612, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Brayden JE Functional roles of KATP channels in vascular smooth muscle. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 29: 312–316, 2002. - PubMed
-
- Budel S, Bartlett IS, Segal SS. Homocellular conduction along endothelium and smooth muscle of arterioles in hamster cheek pouch: unmasking an NO wave. Circ Res 93: 61–68, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Chatterjee S, Al Mehdi AB, Levitan I, Stevens T, Fisher AB. Shear stress increases expression of a KATP channel in rat and bovine pulmonary vascular endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 285: C959–C967, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Crane GJ, Hines ML, Neild TO. Simulating the spread of membrane potential changes in arteriolar networks. Microcirculation 8: 33–43, 2001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

