Prognostic significance of tumor-infiltrating T-lymphocytes in primary and metastatic lesions of advanced stage ovarian cancer
- PMID: 18791714
- PMCID: PMC11030692
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-008-0583-5
Prognostic significance of tumor-infiltrating T-lymphocytes in primary and metastatic lesions of advanced stage ovarian cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Ovarian cancer patients with intra-tumoral CD3(+) T-lymphocytes in primary tumor tissue have a better prognosis. This study aims to analyze the presence and relative influence of three important T-lymphocyte subsets, tumor-infiltrating CD8(+) cytotoxic T-lymphocytes (CTL), CD45R0(+) memory T-lymphocytes, and FoxP3(+) regulatory T-lymphocytes (Treg), in primary tumor tissue and omental metastases of patients with ovarian cancer.
Experimental design: The number of CD8(+), CD45R0(+), and FoxP3(+) T-lymphocytes was determined by immunohistochemistry on a tissue micro array containing ovarian tumor tissue and/or omental metastases obtained at primary debulking surgery from 306 FIGO stage I-IV ovarian cancer patients. Immunohistochemistry data were correlated to clinicopathological parameters and survival data.
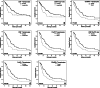
Results: High number of CD8(+) CTL and a high CD8(+)/FoxP3(+) ratio in ovarian-derived tumor tissue were associated with increased disease-specific survival and proved to be independent prognostic factors in multivariate analyses. In advanced stage patients, the presence of CD8(+) CTL, CD45R0(+) memory T-lymphocytes, FoxP3(+) Treg or a high CD8(+)/FoxP3(+) ratio in ovarian-derived tumor tissue was associated with an increased disease specific survival in univariate analysis, as was the presence of CD45R0(+) memory T-lymphocytes and FoxP3(+) Treg in omental metastases. Furthermore, in advanced stage patients CD8(+) cytotoxic and FoxP3(+) regulatory T-lymphocytes infiltrating ovarian-derived tumor tissue were independent predictors of increased prognosis.
Conclusions: T-lymphocytes infiltrating primary and metastatic ovarian cancer sites are associated with improved prognosis. These associations are especially distinct in advanced stage patients, underlining the potential for immunotherapy as a broadly applicable therapeutic strategy.
Figures

References
-
- Alvaro T, Lejeune M, Salvado MT, Bosch R, Garcia JF, Jaen J, Banham AH, Roncador G, Montalban C, Piris MA. Outcome in Hodgkin’s lymphoma can be predicted from the presence of accompanying cytotoxic and regulatory T cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:1467–1473. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1869. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Badoual C, Hans S, Rodriguez J, Peyrard S, Klein C, Agueznay NH, Mosseri V, Laccourreye O, Bruneval P, Fridman WH, Brasnu DF, Tartour E. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating CD4+ T-cell subpopulations in head and neck cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:465–472. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1886. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

