An attentional blink for sequentially presented targets: evidence in favor of resource depletion accounts
- PMID: 18792508
- PMCID: PMC3644218
- DOI: 10.3758/pbr.15.4.809
An attentional blink for sequentially presented targets: evidence in favor of resource depletion accounts
Abstract
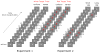
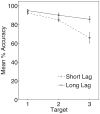
Several accounts of the attentional blink (AB) have postulated that this dual-target deficit occurs because of limited-capacity attentional resources being devoted to processing the first target at the expense of the second (resource depletion accounts; e.g., Chun & Potter, 1995). Recent accounts have challenged this model (e.g., Di Lollo, Kawahara, Ghorashi, & Enns, 2005; Olivers, van der Stigchel, & Hulleman, 2007), proposing instead that the AB occurs because of subjects' inability to maintain appropriate levels of attentional controlwhen targets are separated by distractors. Accordingly, the AB is eliminated when three targets from the same attentional set are presented sequentially in a rapid serial visual presentation (RSVP) stream. However, under such conditions poorer identification of the first target is typically observed, hinting at a potential trade-off between the first and subsequent target performances. Consistent with this hypothesis, the present study shows that an AB is observed for successive targets from the same attentional set in an RSVP stream when the first target powerfully captures attention. These results suggest that resource depletion contributes significantly to the AB.
Figures

Comment in
-
The attentional blink: increasing target salience provides no evidence for resource depletion. A commentary on Dux, Asplund, and Marois (2008).Psychon Bull Rev. 2009 Feb;16(1):214-8; discussion 219-24. doi: 10.3758/PBR.16.1.214. Psychon Bull Rev. 2009. PMID: 19145034
References
-
- Brainard DH. The psychophysics toolbox. Spatial Vision. 1997;10:433–436. - PubMed
-
- Broadbent DE, Broadbent MHP. From detection to identification: Response to multiple targets in rapid serial visual presentation. Perception & Psychophysics. 1987;42:105–113. - PubMed
-
- Chun MM, Potter MC. A two-stage model for multiple target detection in rapid serial visual presentation. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance. 1995;21:109–127. - PubMed
-
- Di Lollo V, Kawahara J, Ghorashi SMS, Enns JT. The attentional blink: Resource depletion or temporary loss of control. Psychological Research. 2005;69:191–200. - PubMed
-
- Jolicoeur P. Modulation of the attentional blink by online response selection: Evidence from speeded and unspeeded task1 decisions. Memory & Cognition. 1998;26:1014–1032. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
