Endocytosis and intracellular trafficking of ErbBs
- PMID: 18793634
- PMCID: PMC2605728
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2008.08.013
Endocytosis and intracellular trafficking of ErbBs
Abstract
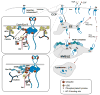
This review article describes the pathways and mechanisms of endocytosis and post-endocytic sorting of the EGF receptor (EGFR/ErbB1) and other members of the ErbB family. Growth factor binding to EGFR accelerates its internalization through clathrin-coated pits which is followed by the efficient lysosomal targeting of internalized receptors and results in receptor down-regulation. The role of EGFR interaction with the Grb2 adaptor protein and Cbl ubiquitin ligase, and receptor ubiquitination in the clathrin-dependent internalization and sorting of EGFR in multivesicular endosomes is discussed. Activation and phosphorylation of ErbB2, ErbB3 and ErbB4 also results in their ubiquitination. However, these ErbBs are internalized and targeted to lysosomes less efficiently than EGFR. When overexpressed endocytosis-impaired ErbBs may inhibit the internalization and degradation of EGFR.
Figures
References
-
- Wells A, Welsh JB, Lazar CS, Wiley HS, Gill GN, Rosenfeld MG. Ligand-induced transformation by a noninternalizing epidermal growth factor receptor. Science. 1990;247:962–964. - PubMed
-
- Sorkin A, Von Zastrow M. Signal transduction and endocytosis: close encounters of many kinds. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:600–614. - PubMed
-
- Wiley HS. Trafficking of the ErbB receptors and its influence on signaling. Exp Cell Res. 2003;284:78–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

