Transcription rate of noncoding roX1 RNA controls local spreading of the Drosophila MSL chromatin remodeling complex
- PMID: 18793722
- PMCID: PMC2659721
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mod.2008.08.003
Transcription rate of noncoding roX1 RNA controls local spreading of the Drosophila MSL chromatin remodeling complex
Abstract
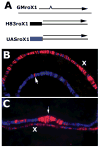
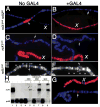
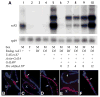
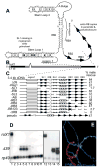
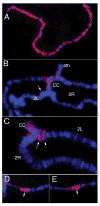
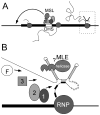
The dosage compensation complex in Drosophila is composed of at least five MSL proteins and two noncoding roX RNAs that bind hundreds of sites along the single male X chromosome. The roX RNAs are transcribed from X-linked genes and their RNA products "paint" the male X. The roX RNAs and bound MSL proteins can spread in cis from sites of roX transcription, but the mechanism controlling spreading is unknown. Here we find that cis spreading from autosomal roX1 transgenes is coupled to the level of roX transcription. Low to moderate transcription favors, and vigorous transcription abolishes local spreading. We constructed a roX1 minigene one third the size of wild type as a starting point for mutagenesis. This allowed us to test which evolutionarily conserved motifs were required for activity. One short repeat element shared between roX1 and roX2 was found to be particularly important. When all copies were deleted, the RNA was inactive and unstable, while extra copies seem to promote local spreading of the MSL complex from sites of roX1 synthesis. We propose that assembly of the MSL proteins onto the extreme 3' region of elongating roX1 transcripts determines whether the MSL complex spreads in cis.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

