Analysis of radiation pneumonitis risk using a generalized Lyman model
- PMID: 18793959
- PMCID: PMC3442942
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.04.053
Analysis of radiation pneumonitis risk using a generalized Lyman model
Erratum in
- Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010 Sep 1;78(1):316-7. Dosage error in article text
Abstract
Purpose: To introduce a version of the Lyman normal-tissue complication probability (NTCP) model adapted to incorporate censored time-to-toxicity data and clinical risk factors and to apply the generalized model to analysis of radiation pneumonitis (RP) risk.
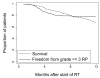
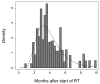
Methods and materials: Medical records and radiation treatment plans were reviewed retrospectively for 576 patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with radiotherapy. The time to severe (Grade >/=3) RP was computed, with event times censored at last follow-up for patients not experiencing this endpoint. The censored time-to-toxicity data were analyzed using the standard and generalized Lyman models with patient smoking status taken into account.
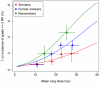
Results: The generalized Lyman model with patient smoking status taken into account produced NTCP estimates up to 27 percentage points different from the model based on dose-volume factors alone. The generalized model also predicted that 8% of the expected cases of severe RP were unobserved because of censoring. The estimated volume parameter for lung was not significantly different from n = 1, corresponding to mean lung dose.
Conclusions: NTCP models historically have been based solely on dose-volume effects and binary (yes/no) toxicity data. Our results demonstrate that inclusion of nondosimetric risk factors and censored time-to-event data can markedly affect outcome predictions made using NTCP models.
Figures

References
-
- Lyman JT. Complication probability as assessed from dose-volume histograms. Radiat Res Suppl. 1985;8:S13–19. - PubMed
-
- Hernando ML, Marks LB, Bentel GC, et al. Radiation-induced pulmonary toxicity: a dose-volume histogram analysis in 201 patients with lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2001;51:650–659. - PubMed
-
- Kahan Z, Csenki M, Varga Z, et al. The risk of early and late lung sequelae after conformal radiotherapy in breast cancer patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;68:673–681. - PubMed
-
- Johansson S, Bjermer L, Franzen L, et al. Effects of ongoing smoking on the development of radiation-induced pneumonitis in breast cancer and oesophagus cancer patients. Radiother Oncol. 1998;49:41–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

