Efficacy, safety and patient-reported outcomes of combination etanercept and sulfasalazine versus etanercept alone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a double-blind randomised 2-year study
- PMID: 18794178
- PMCID: PMC2689524
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2007.087106
Efficacy, safety and patient-reported outcomes of combination etanercept and sulfasalazine versus etanercept alone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a double-blind randomised 2-year study
Abstract
Objective: To determine the efficacy and safety of etanercept and etanercept plus sulfasalazine versus sulfasalazine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) despite sulfasalazine therapy.
Methods: Patients were randomly assigned to etanercept (25 mg twice weekly; sulfasalazine was discontinued at baseline), etanercept plus sulfasalazine (unchanged regimen of 2-3 g/day) or sulfasalazine in a double-blind, randomised, 2-year study in adult patients with active RA despite sulfasalazine therapy. Efficacy was assessed using the American College of Rheumatology criteria, disease activity scores (DAS) and patient-reported outcomes (PRO).
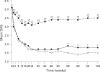
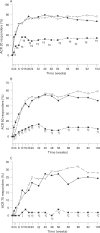
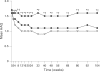
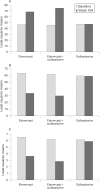
Results: Demographic variables and baseline disease characteristics were comparable among treatment groups; mean DAS 5.1, 5.2 and 5.1 for etanercept (n = 103), etanercept plus sulfasalazine (n = 101) and sulfasalazine (n = 50), respectively. Withdrawal due to lack of efficacy was highest with sulfasalazine (26 (52%) vs 6 (6%) for either etanercept group, p<0.001). Patients receiving etanercept or etanercept plus sulfasalazine had a more rapid initial response, which was sustained at 2 years, than those receiving sulfasalazine: mean DAS 2.8, 2.5 versus 4.5, respectively (p<0.05); ACR 20 response was achieved by 67%, 77% versus 34% of patients, respectively (p<0.01) Overall, PRO followed a similar pattern; a clinically significant improvement in health assessment questionnaire was achieved by 76%, 78% versus 40% of patients, respectively (p<0.01). Commonly reported adverse events occurring in the etanercept groups were injection site reactions and pharyngitis/laryngitis (p<0.01).
Conclusion: Etanercept and etanercept plus sulfasalazine are efficacious for the long-term management of patients with RA. The addition of etanercept or substitution with etanercept should be considered as treatment options for patients not adequately responding to sulfasalazine.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- O’Dell JR. Therapeutic strategies for rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 2004;350:2591–602 - PubMed
-
- Weinblatt ME, Kremer JM, Bankhurst AD, Bulpitt KJ, Fleischmann RM, Fox RI, et al. A trial of etanercept, a recombinant tumor necrosis factor receptor:Fc fusion protein, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving methotrexate. N Engl J Med 1999;340:253–9 - PubMed
-
- Maini R, St Clair EW, Breedveld F, Furst D, Kalden J, Weisman M, et al. Infliximab (chimeric anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving concomitant methotrexate: a randomised phase III trial. ATTRACT Study Group. Lancet 1999;354:1932–9 - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto I, Lee DM, Goldbach-Mansky R, Sumida T, Hitchon CA, Schur PH, et al. Low prevalence of antibodies to glucose-6-phosphate isomerase in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and a spectrum of other chronic autoimmune disorders. Arthritis Rheum 2003;48:944–54 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

