Regulation of caveolin-1 membrane trafficking by the Na/K-ATPase
- PMID: 18794328
- PMCID: PMC2542476
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200712022
Regulation of caveolin-1 membrane trafficking by the Na/K-ATPase
Abstract
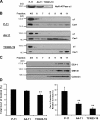
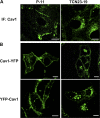
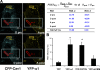
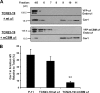
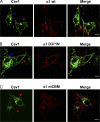
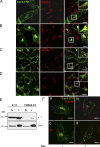
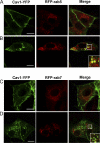
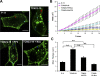
Here, we show that the Na/K-ATPase interacts with caveolin-1 (Cav1) and regulates Cav1 trafficking. Graded knockdown of Na/K-ATPase decreases the plasma membrane pool of Cav1, which results in a significant reduction in the number of caveolae on the cell surface. These effects are independent of the pumping function of Na/K-ATPase, and instead depend on interaction between Na/K-ATPase and Cav1 mediated by an N-terminal caveolin-binding motif within the ATPase alpha1 subunit. Moreover, knockdown of the Na/K-ATPase increases basal levels of active Src and stimulates endocytosis of Cav1 from the plasma membrane. Microtubule-dependent long-range directional trafficking in Na/K-ATPase-depleted cells results in perinuclear accumulation of Cav1-positive vesicles. Finally, Na/K-ATPase knockdown has no effect on processing or exit of Cav1 from the Golgi. Thus, the Na/K-ATPase regulates Cav1 endocytic trafficking and stabilizes the Cav1 plasma membrane pool.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Do Src Kinase and Caveolin Interact Directly with Na,K-ATPase?J Biol Chem. 2016 May 27;291(22):11736-50. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.721084. Epub 2016 Mar 28. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27022017 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Na/K-ATPase expression by cholesterol: isoform specificity and the molecular mechanism.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020 Dec 1;319(6):C1107-C1119. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00083.2020. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32997514 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a pool of non-pumping Na/K-ATPase.J Biol Chem. 2007 Apr 6;282(14):10585-93. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M609181200. Epub 2007 Feb 12. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17296611
-
Molecular mechanisms of Na/K-ATPase-mediated signal transduction.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003 Apr;986:497-503. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb07234.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003. PMID: 12763870 Review.
-
The Na,K-ATPase receptor complex: its organization and membership.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2006;46(3):303-16. doi: 10.1385/cbb:46:3:303. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2006. PMID: 17272855 Review.
Cited by
-
Specialized Functional Diversity and Interactions of the Na,K-ATPase.Front Physiol. 2016 May 25;7:179. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00179. eCollection 2016. Front Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27252653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase cell surface abundance through structural determinants on the α1-subunit.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011 Jan;300(1):C42-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00386.2010. Epub 2010 Nov 3. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21048163 Free PMC article.
-
Brain Na(+), K(+)-ATPase Activity In Aging and Disease.Int J Biomed Sci. 2014 Jun;10(2):85-102. Int J Biomed Sci. 2014. PMID: 25018677 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingolipids affect fibrinogen-induced caveolar transcytosis and cerebrovascular permeability.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014 Jul 15;307(2):C169-79. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00305.2013. Epub 2014 May 14. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24829496 Free PMC article.
-
Novel mutations affecting the Na, K ATPase alpha model complex neurological diseases and implicate the sodium pump in increased longevity.Hum Genet. 2009 Sep;126(3):431-47. doi: 10.1007/s00439-009-0673-2. Epub 2009 May 12. Hum Genet. 2009. PMID: 19455355 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson, R.G. 1998. The caveolae membrane system. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67:199–225. - PubMed
-
- Baker, P.F., and J.S. Willis. 1969. On the number of sodium pumping sites in cell membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 183:646–649. - PubMed
-
- Baker, P.F., and J.S. Willis. 1970. Potassium ions and the binding of cardiac glycosides to mammalian cells. Nature. 226:521–523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

