EPB41L5 functions to post-transcriptionally regulate cadherin and integrin during epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- PMID: 18794329
- PMCID: PMC2542480
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200712086
EPB41L5 functions to post-transcriptionally regulate cadherin and integrin during epithelial-mesenchymal transition
Abstract
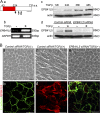
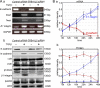
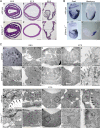
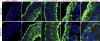
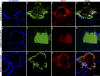
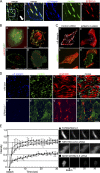
EPB41L5 belongs to the band 4.1 superfamily. We investigate here the involvement of EPB41L5 in epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) during mouse gastrulation. EPB41L5 expression is induced during TGFbeta-stimulated EMT, whereas silencing of EPB41L5 by siRNA inhibits this transition. In EPB41L5 mutants, cell-cell adhesion is enhanced, and EMT is greatly impaired during gastrulation. Moreover, cell attachment, spreading, and mobility are greatly reduced by EPB41L5 deficiency. Gene transcription regulation during EMT occurs normally at the mRNA level; EPB41L5 siRNA does not affect either the decrease in E-cadherin or the increase in integrin expression. However, at the protein level, the decrease in E-cadherin and increase in integrin are inhibited in both EPB41L5 siRNA-treated NMuMG cells and mutant mesoderm. We find that EPB41L5 binds p120ctn through its N-terminal FERM domain, inhibiting p120ctn-E-cadherin binding. EPB41L5 overexpression causes E-cadherin relocalization into Rab5-positive vesicles in epithelial cells. At the same time, EPB41L5 binds to paxillin through its C terminus, enhancing integrin/paxillin association, thereby stimulating focal adhesion formation.
Figures

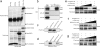
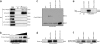
Similar articles
-
NCAM-induced focal adhesion assembly: a functional switch upon loss of E-cadherin.EMBO J. 2008 Oct 8;27(19):2603-15. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.178. Epub 2008 Sep 4. EMBO J. 2008. PMID: 18772882 Free PMC article.
-
Disabled-2 (Dab2) is required for transforming growth factor beta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT).J Biol Chem. 2005 Apr 29;280(17):17540-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M500974200. Epub 2005 Feb 25. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15734730
-
Integrin signaling potentiates transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1) dependent down-regulation of E-Cadherin expression - Important implications for epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) in renal cell carcinoma.Exp Cell Res. 2017 Jun 15;355(2):57-66. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.03.051. Epub 2017 Mar 29. Exp Cell Res. 2017. PMID: 28363829
-
NCAM is at the heart of reciprocal regulation of E-cadherin- and integrin-mediated adhesions via signaling modulation.Dev Cell. 2008 Oct;15(4):494-6. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2008.09.016. Dev Cell. 2008. PMID: 18854134 Review.
-
Cadherins and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2013;116:317-36. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394311-8.00014-5. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2013. PMID: 23481201 Review.
Cited by
-
Making alternative splicing decisions during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT).Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Aug;69(15):2515-26. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-0931-7. Epub 2012 Feb 19. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22349259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EPB41L5 is Associated With the Metastatic Potential of Low-grade Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2019 Sep-Oct;16(5):309-318. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20136. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2019. PMID: 31467225 Free PMC article.
-
Orchestration of mesenchymal plasticity and immune evasiveness via rewiring of the metabolic program in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 3;12:1005566. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1005566. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36408139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complex changes in alternative pre-mRNA splicing play a central role in the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT).Semin Cancer Biol. 2012 Oct;22(5-6):417-27. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2012.04.003. Epub 2012 Apr 23. Semin Cancer Biol. 2012. PMID: 22548723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The adenoviral protein E4orf4: a probing tool to decipher mechanical stress-induced nuclear envelope remodeling in tumor cells.Cell Cycle. 2020 Nov;19(22):2963-2981. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1836441. Epub 2020 Oct 25. Cell Cycle. 2020. PMID: 33103553 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Batlle, E., E. Sancho, C. Franci, D. Dominguez, M. Monfar, J. Baulida, and A. Garcia de Herreros. 2000. The transcription factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in epithelial tumour cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2:84–89. - PubMed
-
- Cano, A., M.A. Perez-Moreno, I. Rodrigo, A. Locascio, M.J. Blanco, M.G. del Barrio, F. Portillo, and M.A. Nieto. 2000. The transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat. Cell Biol. 2:76–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

