The T-box transcription factor Eomes/Tbr2 regulates neurogenesis in the cortical subventricular zone
- PMID: 18794345
- PMCID: PMC2546697
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.475408
The T-box transcription factor Eomes/Tbr2 regulates neurogenesis in the cortical subventricular zone
Abstract
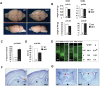
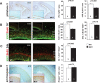
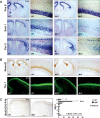
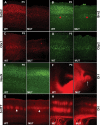
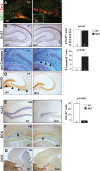
The embryonic subventricular zone (SVZ) is a critical site for generating cortical projection neurons; however, molecular mechanisms regulating neurogenesis specifically in the SVZ are largely unknown. The transcription factor Eomes/Tbr2 is transiently expressed in cortical SVZ progenitor cells. Here we demonstrate that conditional inactivation of Tbr2 during early brain development causes microcephaly and severe behavioral deficits. In Tbr2 mutants the number of SVZ progenitor cells is reduced and the differentiation of upper cortical layer neurons is disturbed. Neurogenesis in the adult dentate gyrus but not the subependymal zone is abolished. These studies establish Tbr2 as a key regulator of neurogenesis in the SVZ.
Figures
References
-
- Altman J., Bayer S.A. Migration and distribution of two populations of hippocampal granule cell precursors during the perinatal and postnatal periods. J. Comp. Neurol. 1990;301:365–381. - PubMed
-
- Ayala R., Shu T., Tsai L.H. Trekking across the brain: The journey of neuronal migration. Cell. 2007;128:29–43. - PubMed
-
- Baala L., Briault S., Etchevers H.C., Laumonnier F., Natiq A., Amiel J., Boddaert N., Picard C., Sbiti A., Asermouh A., et al. Homozygous silencing of T-box transcription factor EOMES leads to microcephaly with polymicrogyria and corpus callosum agenesis. Nat. Genet. 2007;39:454–456. - PubMed
-
- Britanova O., de Juan Romero C., Cheung A., Kwan K.Y., Schwark M., Gyorgy A., Vogel T., Akopov S., Mitkovski M., Agoston D., et al. Satb2 is a postmitotic determinant for upper-layer neuron specification in the neocortex. Neuron. 2008;57:378–392. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
