NMR-spectroscopic screening of spider venom reveals sulfated nucleosides as major components for the brown recluse and related species
- PMID: 18794518
- PMCID: PMC2567178
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0806840105
NMR-spectroscopic screening of spider venom reveals sulfated nucleosides as major components for the brown recluse and related species
Abstract
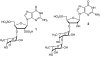
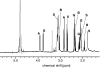
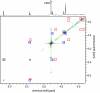
Extensive chemical analyses of spider venoms from many species have revealed complex mixtures of biologically active compounds, of which several have provided important leads for drug development. We have recently shown that NMR spectroscopy can be used advantageously for a direct structural characterization of the small-molecule content of such complex mixtures. Here, we report the application of this strategy to a larger-scale analysis of a collection of spider venoms representing >70 species, which, in combination with mass spectrometric analyses, allowed the identification of a wide range of known, and several previously undescribed, small molecules. These include polyamines, common neurotransmitters, and amino acid derivatives as well as two additional members of a recently discovered family of natural products, the sulfated nucleosides. In the case of the well studied brown recluse spider, Loxosceles reclusa, sulfated guanosine derivatives were found to comprise the major small-molecule components of the venom.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Cobas JC, Groves P, Martin-Pastor M, De Capua A. New applications, processing methods and pulse sequences using diffusion NMR. Curr Anal Chem. 2005;1:289–305.
-
- Halouska S, Powers R. Negative impact of noise on the principal component analysis of NMR data. J Magn Res. 2006;178:88–95. - PubMed
-
- Dossey AT, Walse SS, Rocca JR, Edison AS. Single-insect NMR: A new tool to probe chemical biodiversity. Am Chem Soc Chem Biol. 2006;1:511–514. - PubMed
-
- Zhang F, Dossey AT, Zachariah C, Edison AS, Bruschweiler R. Strategy for automated analysis of dynamic metabolic mixtures by NMR. Application to an insect venom. Anal Chem. 2007;79:7748–7752. - PubMed
-
- Taggi AE, Meinwald J, Schroeder FC. A new approach to natural products discovery exemplified by the identification of sulfated nucleosides in spider venom. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:10364–10369. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

