PI3K pathway alterations in cancer: variations on a theme
- PMID: 18794884
- PMCID: PMC3398461
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2008.245
PI3K pathway alterations in cancer: variations on a theme
Abstract
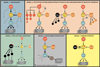
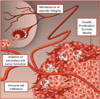
The high frequency of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway alterations in cancer has led to a surge in the development of PI3K inhibitors. Many of these targeted therapies are currently in clinical trials and show great promise for the treatment of PI3K-addicted tumors. These recent developments call for a re-evaluation of the oncogenic mechanisms behind PI3K pathway alterations. This pathway is unique in that every major node is frequently mutated or amplified in a wide variety of solid tumors. Receptor tyrosine kinases upstream of PI3K, the p110 alpha catalytic subunit of PI3K, the downstream kinase, AKT, and the negative regulator, PTEN, are all frequently altered in cancer. In this review, we will examine the oncogenic properties of these genetic alterations to understand whether they are redundant or distinct and propose treatment strategies tailored for these genetic lesions.
Figures

References
-
- Abubaker J, Bavi P, Al-Harbi S, Ibrahim M, Siraj AK, Al-Sanea N, et al. Clinicopathological analysis of colorectal cancers with PIK3CA mutations in Middle Eastern population. Oncogene. 2008;27:3539–3545. - PubMed
-
- Arteaga CL. EGF receptor mutations in lung cancer: from humans to mice and maybe back to humans. Cancer Cell. 2006;9:421–423. - PubMed
-
- Bachman KE, Argani P, Samuels Y, Silliman N, Ptak J, Szabo S, et al. The PIK3CA gene is mutated with high frequency in human breast cancers. Cancer Biol Ther. 2004;3:772–775. - PubMed
-
- Barault L, Veyrie N, Jooste V, Lecorre D, Chapusot C, Ferraz JM, et al. Mutations in the RAS-MAPK, PI(3)K (phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase) signaling network correlate with poor survival in a population-based series of colon cancers. Int J Cancer. 2008;122:2255–2259. - PubMed
-
- Barnes KR, Blois J, Smith A, Yuan H, Reynolds F, Weissleder R, et al. Fate of a bioactive fluorescent wortmannin derivative in cells. Bioconjug Chem. 2008;19:130–137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

