Intradural extramedullary primary hydatid cyst of the spine in a child: a very rare presentation
- PMID: 18795342
- PMCID: PMC2899549
- DOI: 10.1007/s00586-008-0777-8
Intradural extramedullary primary hydatid cyst of the spine in a child: a very rare presentation
Abstract
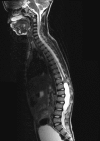
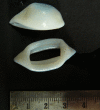
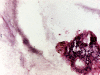
Spinal hydatid cyst is a serious but fortunately uncommon manifestation of the parasite Echinococcus, involving less than 1% patients with hydatid disease. Intradural hydatid cysts are extremely rare compared to other types of spinal hydatid cysts. We report a rare case of intradural, extramedullary spinal hydatid cyst in a 9-year-old male boy, who presented with weakness of both lower limbs for the last 4 months that was confirmed histopathologically; a better understanding of this rare but clinically challenging disease is intended by reporting this case.
Figures

Comment in
-
Intradural extramedullary primary hydatid cyst of the spine in a child: a very rare presentation.Eur Spine J. 2009 Aug;18(8):1234-5; author reply 1236. doi: 10.1007/s00586-009-1006-9. Epub 2009 Apr 25. Eur Spine J. 2009. PMID: 19396476 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

