MATERNALLY EXPRESSED PAB C-TERMINAL, a novel imprinted gene in Arabidopsis, encodes the conserved C-terminal domain of polyadenylate binding proteins
- PMID: 18796636
- PMCID: PMC2570725
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.108.061929
MATERNALLY EXPRESSED PAB C-TERMINAL, a novel imprinted gene in Arabidopsis, encodes the conserved C-terminal domain of polyadenylate binding proteins
Abstract
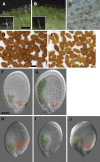
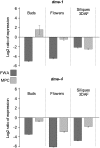
Parental imprinting is important for seed development, but few imprinted genes have been identified in plants. The four known imprinted genes in Arabidopsis thaliana encode transcriptional regulators. Here, we describe a novel imprinted gene, MATERNALLY EXPRESSED PAB C-TERMINAL (MPC), which encodes the C-terminal domain of poly(A) binding proteins (PABPs). PABPs play roles in mRNA stability and translation. MPC interacts with proteins that also interact with the C-terminal domain of typical PABPs, suggesting that MPC may regulate translation by modulating PABP activity. In the endosperm, MPC is expressed only from the maternal allele. Reduction of MPC expression affects seed development. In dna methyltransferase1 (met1) mutants, MPC is ectopically expressed, and the paternal allele is active in the endosperm. CGs in the 5' flanking region and gene body of MPC lose methylation in a met1 background. Both regions are required to confer imprinted reporter expression, suggesting that the gene body contains imprinting control region elements. In Arabidopsis, DEMETER (DME) activates expression of maternal alleles. MPC expression is reduced in flowers and seeds in a dme-4 mutant but only after fertilization in dme-1. We conclude that other factors along with DME promote MPC expression and that DME has indirect effects on imprinted gene expression in endosperm.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Control of Paternally Expressed Imprinted UPWARD CURLY LEAF1, a Gene Encoding an F-Box Protein That Regulates CURLY LEAF Polycomb Protein, in the Arabidopsis Endosperm.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 17;10(2):e0117431. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117431. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25689861 Free PMC article.
-
DEMETER, a DNA glycosylase domain protein, is required for endosperm gene imprinting and seed viability in arabidopsis.Cell. 2002 Jul 12;110(1):33-42. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00807-3. Cell. 2002. PMID: 12150995
-
Identification of imprinted genes subject to parent-of-origin specific expression in Arabidopsis thaliana seeds.BMC Plant Biol. 2011 Aug 12;11:113. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-11-113. BMC Plant Biol. 2011. PMID: 21838868 Free PMC article.
-
[Genomic imprinting and seed development].Yi Chuan. 2005 Jul;27(4):665-70. Yi Chuan. 2005. PMID: 16120596 Review. Chinese.
-
[Imprinting genes and it's expression in Arabidopsis].Yi Chuan. 2010 Jul;32(7):670-6. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1005.2010.00670. Yi Chuan. 2010. PMID: 20650847 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Two key genomic regions harbour QTLs for salinity tolerance in ICCV 2 × JG 11 derived chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) recombinant inbred lines.BMC Plant Biol. 2015 May 22;15:124. doi: 10.1186/s12870-015-0491-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2015. PMID: 25994494 Free PMC article.
-
Roles, and establishment, maintenance and erasing of the epigenetic cytosine methylation marks in plants.J Genet. 2013 Dec;92(3):629-66. doi: 10.1007/s12041-013-0273-8. J Genet. 2013. PMID: 24371187 Review.
-
Genomic imprinting, methylation and parent-of-origin effects in reciprocal hybrid endosperm of castor bean.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jun;42(11):6987-98. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku375. Epub 2014 May 5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24799438 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide screening and analysis of imprinted genes in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) endosperm.DNA Res. 2018 Dec 1;25(6):629-640. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dsy030. DNA Res. 2018. PMID: 30272113 Free PMC article.
-
Active DNA demethylation: mechanism and role in plant development.Plant Cell Rep. 2018 Jan;37(1):77-85. doi: 10.1007/s00299-017-2215-z. Epub 2017 Oct 12. Plant Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 29026973 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alonso, J.M., et al. (2003). Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301 653–657. - PubMed
-
- Bravo, J., Aguilar-Henonin, L., Olmedo, G., and Guzmán, P. (2005). Four distinct classes of proteins as interaction partners of the PABC domain of Arabidopsis thaliana poly(A)-binding proteins. Mol. Genet. Genomics 272 651–665. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

