Inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitor SD-3651 reduces proteinuria in MRL/lpr mice deficient in the NOS2 gene
- PMID: 18797415
- PMCID: PMC2637653
- DOI: 10.2310/JIM.0b013e3181889e13
Inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitor SD-3651 reduces proteinuria in MRL/lpr mice deficient in the NOS2 gene
Abstract
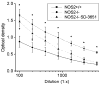
Several studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of arginine analog nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor therapy in preventing and treating murine lupus nephritis. However, MRL/MpJ-FAS (MRL/lpr) mice lacking a functional NOS2 (inducible NOS [iNOS]) gene (NOS2) develop proliferative glomerulonephritis in a fashion similar to their wild-type (wt) littermates. This finding suggests that the effect of arginine analog NOS inhibitors is through a non-iNOS-mediated mechanism. This study was designed to address this hypothesis.NOS2 mice were given either vehicle or a NOS inhibitor (SD-3651) to determine if pharmacological NOS inhibition prevented glomerulonephritis, using wt mice as positive controls. Urine was collected fortnightly to measure albumin. At the time of full disease expression in wt mice, all mice were killed, and renal tissue was examined for light, immunofluorescence, and electron microscopic evidence of disease. Serum was analyzed for anti-double-stranded DNA antibody production.NOS2 mice had higher serum anti-double-stranded DNA antibody antibody levels than those of wt mice. SD-3651 therapy reduced proteinuria, glomerular immunoglobulin G deposition, and electron microscopic evidence of podocytopathy and endothelial cell swelling without affecting proliferative lesions by light microscopy.These studies confirm that genetic iNOS deficiency alone is insufficient to prevent proliferative glomerulonephritis and suggest that iNOS activity may inhibit autoantibody production. These results also suggest that SD-3651 therapy acts via a non-iNOS-mediated mechanism to prevent endothelial cell and podocyte pathology. Studies that elucidate this mechanism could provide a useful drug target for the treatment of nephritis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase reduces crescentic and necrotic glomerular lesions, reactive oxygen production, and MCP1 production in murine lupus nephritis.PLoS One. 2013 May 31;8(5):e64650. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064650. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23741359 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of renal disease in MRL/lpr mice by pharmacologic inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase.Kidney Int. 2002 Mar;61(3):839-46. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2002.00230.x. Kidney Int. 2002. PMID: 11849435
-
Effects of complement factor D deficiency on the renal disease of MRL/lpr mice.Kidney Int. 2004 Jan;65(1):129-38. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.00371.x. Kidney Int. 2004. PMID: 14675043
-
Nitric oxide as an inflammatory mediator in autoimmune MRL-lpr/lpr mice.Environ Health Perspect. 1998 Oct;106 Suppl 5(Suppl 5):1131-7. doi: 10.1289/ehp.98106s51131. Environ Health Perspect. 1998. PMID: 9788887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of genetic knockouts to modulate disease expression in a murine model of lupus, MRL/lpr mice.Immunol Res. 2002;25(2):143-53. doi: 10.1385/ir:25:2:143. Immunol Res. 2002. PMID: 11999168 Review.
Cited by
-
Lipopolysaccharide induces inducible nitric oxide synthase-dependent podocyte dysfunction via a hypoxia-inducible factor 1α and cell division control protein 42 and Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 pathway.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Jul;84:185-195. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.02.031. Epub 2015 Mar 9. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 25765888 Free PMC article.
-
Immunotherapy of diffuse gliomas: biological background, current status and future developments.Brain Pathol. 2009 Oct;19(4):674-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2009.00315.x. Brain Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19744040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone ameliorates disease activity in an induced murine lupus-like model.Clin Exp Immunol. 2014 Aug;177(2):381-90. doi: 10.1111/cei.12336. Clin Exp Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24666423 Free PMC article.
-
NADPH oxidase and nitric oxide synthase-dependent superoxide production is increased in proliferative lupus nephritis.Lupus. 2013 Nov;22(13):1361-70. doi: 10.1177/0961203313507988. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Lupus. 2013. PMID: 24106214 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase reduces crescentic and necrotic glomerular lesions, reactive oxygen production, and MCP1 production in murine lupus nephritis.PLoS One. 2013 May 31;8(5):e64650. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064650. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23741359 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oates JC, Gilkeson GS. Nitric oxide in SLE. In: Tsokos GC, Gordon C, Smolen JS, editors. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Companion to Rheumatology. 1. Philadelphia, PA: Mosby Elsevier; 2007.
-
- Weinberg JB, Granger DL, Pisetsky DS, et al. The role of nitric oxide in the pathogenesis of spontaneous murine autoimmune disease: increased nitric oxide production and nitric oxide synthase expression in MRL-lpr/lpr mice, and reduction of spontaneous glomerulonephritis and arthritis by orally administered NG-monomethyl-L-arginine. J Exp Med. 1994;179:651–660. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reilly CM, Farrelly LW, Viti D, et al. Modulation of renal disease in MRL/lpr mice by pharmacologic inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Kidney Int. 2002;61:839–846. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

