Screening for Wilson disease in acute liver failure: a comparison of currently available diagnostic tests
- PMID: 18798336
- PMCID: PMC4881751
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.22446
Screening for Wilson disease in acute liver failure: a comparison of currently available diagnostic tests
Abstract
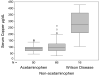
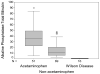
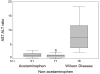
Acute liver failure (ALF) due to Wilson disease (WD) is invariably fatal without emergency liver transplantation. Therefore, rapid diagnosis of WD should aid prompt transplant listing. To identify the best method for diagnosis of ALF due to WD (ALF-WD), data and serum were collected from 140 ALF patients (16 with WD), 29 with other chronic liver diseases and 17 with treated chronic WD. Ceruloplasmin (Cp) was measured by both oxidase activity and nephelometry and serum copper levels by atomic absorption spectroscopy. In patients with ALF, a serum Cp <20 mg/dL by the oxidase method provided a diagnostic sensitivity of 21% and specificity of 84% while, by nephelometry, a sensitivity of 56% and specificity of 63%. Serum copper levels exceeded 200 microg/dL in all ALF-WD patients measured (13/16), but were also elevated in non-WD ALF. An alkaline phosphatase (AP) to total bilirubin (TB) ratio <4 yielded a sensitivity of 94%, specificity of 96%, and a likelihood ratio of 23 for diagnosing fulminant WD. In addition, an AST:ALT ratio >2.2 yielded a sensitivity of 94%, a specificity of 86%, and a likelihood ratio of 7 for diagnosing fulminant WD. Combining the tests provided a diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of 100%.
Conclusion: Conventional WD testing utilizing serum ceruloplasmin and/or serum copper levels are less sensitive and specific in identifying patients with ALF-WD than other available tests. More readily available laboratory tests including alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin and serum aminotransferases by contrast provides the most rapid and accurate method for diagnosis of ALF due to WD.
Figures





Comment in
-
Rapid diagnosis of Wilson disease in acute liver failure: no more waiting for the ceruloplasmin level?Hepatology. 2008 Oct;48(4):1030-2. doi: 10.1002/hep.22587. Hepatology. 2008. PMID: 18821595 No abstract available.
-
Screening for Wilson's disease in acute liver failure: a comparison of currently available diagnostic tests.Hepatology. 2009 Jul;50(1):329. doi: 10.1002/hep.22949. Hepatology. 2009. PMID: 19333910 No abstract available.
-
Values for upper limit of normal should be given for liver enzymes.Hepatology. 2009 May;49(5):1783-4; author reply 1784. doi: 10.1002/hep.22788. Hepatology. 2009. PMID: 19402113 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ostapowicz G, Fontana RJ, Schiodt FV, Larson A, Davern TJ, Han SH, McCashland TM, Shakil AO, Hay JE, Hynan L, Crippin JS, Blei AT, Samuel G, Reisch J, Lee WM, U.S. Acute Liver Failure Study Group Results of a prospective study of acute liver failure at 17 tertiary care centers in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 2002;137:947–54. - PubMed
-
- Roberts E, Schilsky ML. A practice guideline on Wilson disease. Hepatology. 2003;37:1475–1492. - PubMed
-
- Schilsky ML, Sternlieb I. Overcoming obstacles to the diagnosis of Wilson’s disease. Gastroenterology. 1997;113:350–353. - PubMed
-
- Willson RA, Clayson KJ, Leon S. Unmeasurable serum alkaline phosphatase activity in Wilson’s disease associated with fulminant hepatic failure and hemolysis. Hepatology. 1987;7:613–615. - PubMed
-
- Willson RA, Hartleb M. Fulminant wilsonian hepatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1988;83:1309–1310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
