SARS-coronavirus replication is supported by a reticulovesicular network of modified endoplasmic reticulum
- PMID: 18798692
- PMCID: PMC2535663
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060226
SARS-coronavirus replication is supported by a reticulovesicular network of modified endoplasmic reticulum
Abstract
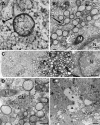
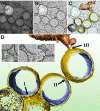
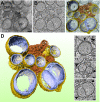
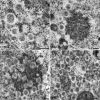
Positive-strand RNA viruses, a large group including human pathogens such as SARS-coronavirus (SARS-CoV), replicate in the cytoplasm of infected host cells. Their replication complexes are commonly associated with modified host cell membranes. Membrane structures supporting viral RNA synthesis range from distinct spherular membrane invaginations to more elaborate webs of packed membranes and vesicles. Generally, their ultrastructure, morphogenesis, and exact role in viral replication remain to be defined. Poorly characterized double-membrane vesicles (DMVs) were previously implicated in SARS-CoV RNA synthesis. We have now applied electron tomography of cryofixed infected cells for the three-dimensional imaging of coronavirus-induced membrane alterations at high resolution. Our analysis defines a unique reticulovesicular network of modified endoplasmic reticulum that integrates convoluted membranes, numerous interconnected DMVs (diameter 200-300 nm), and "vesicle packets" apparently arising from DMV merger. The convoluted membranes were most abundantly immunolabeled for viral replicase subunits. However, double-stranded RNA, presumably revealing the site of viral RNA synthesis, mainly localized to the DMV interior. Since we could not discern a connection between DMV interior and cytosol, our analysis raises several questions about the mechanism of DMV formation and the actual site of SARS-CoV RNA synthesis. Our data document the extensive virus-induced reorganization of host cell membranes into a network that is used to organize viral replication and possibly hide replicating RNA from antiviral defense mechanisms. Together with biochemical studies of the viral enzyme complex, our ultrastructural description of this "replication network" will aid to further dissect the early stages of the coronavirus life cycle and its virus-host interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

