Identification of COUP-TFII orphan nuclear receptor as a retinoic acid-activated receptor
- PMID: 18798693
- PMCID: PMC2535662
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060227
Identification of COUP-TFII orphan nuclear receptor as a retinoic acid-activated receptor
Abstract
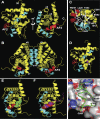
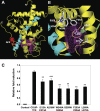
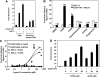
The chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter-transcription factors (COUP-TFI and II) make up the most conserved subfamily of nuclear receptors that play key roles in angiogenesis, neuronal development, organogenesis, cell fate determination, and metabolic homeostasis. Although the biological functions of COUP-TFs have been studied extensively, little is known of their structural features or aspects of ligand regulation. Here we report the ligand-free 1.48 A crystal structure of the human COUP-TFII ligand-binding domain. The structure reveals an autorepressed conformation of the receptor, where helix alpha10 is bent into the ligand-binding pocket and the activation function-2 helix is folded into the cofactor binding site, thus preventing the recruitment of coactivators. In contrast, in multiple cell lines, COUP-TFII exhibits constitutive transcriptional activity, which can be further potentiated by nuclear receptor coactivators. Mutations designed to disrupt cofactor binding, dimerization, and ligand binding, substantially reduce the COUP-TFII transcriptional activity. Importantly, retinoid acids are able to promote COUP-TFII to recruit coactivators and activate a COUP-TF reporter construct. Although the concentration needed is higher than the physiological levels of retinoic acids, these findings demonstrate that COUP-TFII is a ligand-regulated nuclear receptor, in which ligands activate the receptor by releasing it from the autorepressed conformation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
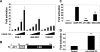



References
-
- Beato M, Herrlich P, Schutz G. Steroid hormone receptors: many actors in search of a plot. Cell. 1995;83:851–857. - PubMed
-
- Mangelsdorf DJ, Evans RM. The RXR heterodimers and orphan receptors. Cell. 1995;83:841–850. - PubMed
-
- Kliewer SA, Lehmann JM, Willson TM. Orphan nuclear receptors: shifting endocrinology into reverse. Science. 1999;284:757–760. - PubMed
-
- Tsai SY, Tsai MJ. Chick ovalbumin upstream promoter-transcription factors (COUP-TFs): coming of age. Endocr Rev. 1997;18:229–240. - PubMed
-
- Germain P, Staels B, Dacquet C, Spedding M, Laudet V. Overview of nomenclature of nuclear receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 2006;58:685–704. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK066202/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HD017379/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD17379/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- DK71662/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01-DK59820/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK059820/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK045641/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL076448/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK045641/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL089301/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK071662/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK66202/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL076448/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK45641/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL89301/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD017379/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

