Mechanisms and consequences of dendritic cell migration
- PMID: 18799141
- PMCID: PMC2818978
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.08.006
Mechanisms and consequences of dendritic cell migration
Abstract
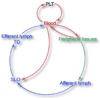
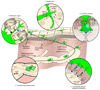
Dendritic cells (DCs) are critical for adaptive immunity and tolerance. Most DCs are strategically positioned as immune sentinels poised to respond to invading pathogens in tissues throughout the body. Differentiated DCs and their precursors also circulate in blood and can get rapidly recruited to sites of challenge. Within peripheral tissues, DCs collect antigenic material and then traffic to secondary lymphoid organs, where they communicate with lymphocytes to orchestrate adaptive immune responses. Hence, the migration and accurate positioning of DCs is indispensable for immune surveillance. Here, we review the molecular traffic signals that govern the migration of DCs throughout their life cycle.
Figures


References
-
- Antonopoulos C, Cumberbatch M, Dearman RJ, Daniel RJ, Kimber I, Groves RW. Functional caspase-1 is required for Langerhans cell migration and optimal contact sensitization in mice. J. Immunol. 2001;166:3672–3677. - PubMed
-
- Auffray C, Fogg D, Garfa M, Elain G, Join-Lambert O, Kayal S, Sarnacki S, Cumano A, Lauvau G, Geissmann F. Monitoring of blood vessels and tissues by a population of monocytes with patrolling behavior. Science. 2007;317:666–670. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

