Type 1 inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors mediate UTP-induced cation currents, Ca2+ signals, and vasoconstriction in cerebral arteries
- PMID: 18799650
- PMCID: PMC2585000
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00362.2008
Type 1 inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors mediate UTP-induced cation currents, Ca2+ signals, and vasoconstriction in cerebral arteries
Erratum in
- Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009 Jul;297(1):C226
Abstract
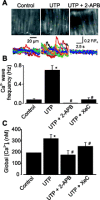
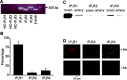
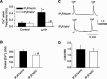
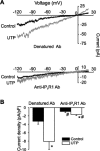
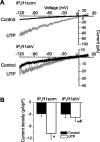
Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors (IP(3)Rs) regulate diverse physiological functions, including contraction and proliferation. There are three IP(3)R isoforms, but their functional significance in arterial smooth muscle cells is unclear. Here, we investigated relative expression and physiological functions of IP(3)R isoforms in cerebral artery smooth muscle cells. We show that 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate and xestospongin C, membrane-permeant IP(3)R blockers, reduced Ca(2+) wave activation and global intracellular Ca(2+) ([Ca(2+)](i)) elevation stimulated by UTP, a phospholipase C-coupled purinergic receptor agonist. Quantitative PCR, Western blotting, and immunofluorescence indicated that all three IP(3)R isoforms were expressed in acutely isolated cerebral artery smooth muscle cells, with IP(3)R1 being the most abundant isoform at 82% of total IP(3)R message. IP(3)R1 knockdown with short hairpin RNA (shRNA) did not alter baseline Ca(2+) wave frequency and global [Ca(2+)](i) but abolished UTP-induced Ca(2+) wave activation and reduced the UTP-induced global [Ca(2+)](i) elevation by approximately 61%. Antibodies targeting IP(3)R1 and IP(3)R1 knockdown reduced UTP-induced nonselective cation current (I(cat)) activation. IP(3)R1 knockdown also reduced UTP-induced vasoconstriction in pressurized arteries with both intact and depleted sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca(2+) by approximately 45%. These data indicate that IP(3)R1 is the predominant IP(3)R isoform expressed in rat cerebral artery smooth muscle cells. IP(3)R1 stimulation contributes to UTP-induced I(cat) activation, Ca(2+) wave generation, global [Ca(2+)](i) elevation, and vasoconstriction. In addition, IP(3)R1 activation constricts cerebral arteries in the absence of SR Ca(2+) release by stimulating plasma membrane I(cat).
Figures


References
-
- Acharya JK, Jalink K, Hardy RW, Hartenstein V, Zuker CS. InsP3 receptor is essential for growth and differentiation but not for vision in Drosophila Neuron 18: 881–887, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Albert AP, Large WA. Store-operated Ca2+-permeable non-selective cation channels in smooth muscle cells. Cell Calcium 33: 345–356, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Blatter LA, Wier WG. Agonist-induced [Ca2+]i waves and Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release in mammalian vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 263: H576–H586, 1992 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

