Structural determinants for membrane association and dynamic organization of the hepatitis C virus NS3-4A complex
- PMID: 18799730
- PMCID: PMC2567209
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0807298105
Structural determinants for membrane association and dynamic organization of the hepatitis C virus NS3-4A complex
Abstract
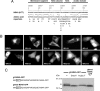
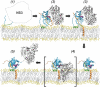
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS3-4A is a membrane-associated multifunctional protein harboring serine protease and RNA helicase activities. It is an essential component of the HCV replication complex and a prime target for antiviral intervention. Here, we show that membrane association and structural organization of HCV NS3-4A are ensured in a cooperative manner by two membrane-binding determinants. We demonstrate that the N-terminal 21 amino acids of NS4A form a transmembrane alpha-helix that may be involved in intramembrane protein-protein interactions important for the assembly of a functional replication complex. In addition, we demonstrate that amphipathic helix alpha(0), formed by NS3 residues 12-23, serves as a second essential determinant for membrane association of NS3-4A, allowing proper positioning of the serine protease active site on the membrane. These results allowed us to propose a dynamic model for the membrane association, processing, and structural organization of NS3-4A on the membrane. This model has implications for the functional architecture of the HCV replication complex, proteolytic targeting of host factors, and drug design.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


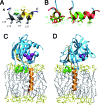
References
-
- Moradpour D, Penin F, Rice CM. Replication of hepatitis C virus. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2007;5:453–463. - PubMed
-
- De Francesco R, Steinkühler C. Structure and function of the hepatitis C virus NS3-NS4A serine protease. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2000;242:149–169. - PubMed
-
- Kim JL, et al. Crystal structure of the hepatitis C virus NS3 protease domain complexed with a synthetic NS4A cofactor peptide. Cell. 1996;87:343–355. - PubMed
-
- Yao N, et al. Molecular views of viral polyprotein processing revealed by the crystal structure of the hepatitis C virus bifunctional protease-helicase. Structure Fold Des. 1999;7:1353–1363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

