The Parkinson's disease genes pink1 and parkin promote mitochondrial fission and/or inhibit fusion in Drosophila
- PMID: 18799731
- PMCID: PMC2567186
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0803998105
The Parkinson's disease genes pink1 and parkin promote mitochondrial fission and/or inhibit fusion in Drosophila
Abstract
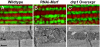
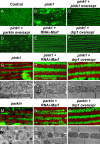
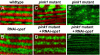
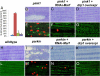
Mutations in PTEN-induced kinase 1 (pink1) or parkin cause autosomal-recessive and some sporadic forms of Parkinson's disease. pink1 acts upstream of parkin in a common genetic pathway to regulate mitochondrial integrity in Drosophila. Mitochondrial morphology is maintained by a dynamic balance between the opposing actions of mitochondrial fusion, controlled by Mitofusin (mfn) and Optic atrophy 1 (opa1), and mitochondrial fission, controlled by drp1. Here, we explore interactions between pink1/parkin and the mitochondrial fusion/fission machinery. Muscle-specific knockdown of the fly homologue of Mfn (Marf) or opa1, or overexpression of drp1, results in significant mitochondrial fragmentation. Mfn-knockdown flies also display altered cristae morphology. Interestingly, knockdown of Mfn or opa1 or overexpression of drp1, rescues the phenotypes of muscle degeneration, cell death, and mitochondrial abnormalities in pink1 or parkin mutants. In the male germline, we also observe genetic interactions between pink1 and the testes-specific mfn homologue fuzzy onion, and between pink1 and drp1. Our data suggest that the pink1/parkin pathway promotes mitochondrial fission and/or inhibits fusion by negatively regulating mfn and opa1 function, and/or positively regulating drp1. However, pink1 and parkin mutant flies show distinct mitochondrial phenotypes from drp1 mutant flies, and flies carrying a heterozygous mutation in drp1 enhance the pink1-null phenotype, resulting in lethality. These results suggest that pink1 and parkin are likely not core components of the drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission machinery. Modification of fusion and fission may represent a novel therapeutic strategy for Parkinson's disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Dauer W, Przedborski S. Parkinson's disease: Mechanisms and models. Neuron. 2003;39:889–909. - PubMed
-
- Langston JW, et al. Chronic Parkinsonism in humans due to a product of meperidine-analog synthesis. Science. 1983;219:979–980. - PubMed
-
- Sherer TB, Betarbet R, Greenamyre JT. Environment, mitochondria, and Parkinson's disease. Neuroscientist. 2002;8:192–197. - PubMed
-
- Dodson MW, Guo M. Pink1, parkin, DJ-1 and mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2007;17:331–337. - PubMed
-
- Wood-Kaczmar A, Gandhi S, Wood NW. Understanding the molecular causes of Parkinson's disease. Trends Mol Med. 2006;12:521–528. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

