Chemical probes for histone-modifying enzymes
- PMID: 18800048
- PMCID: PMC2908280
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.111
Chemical probes for histone-modifying enzymes
Abstract
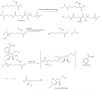
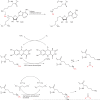
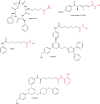
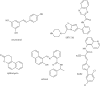
The histone-modifying enzymes that catalyze reversible lysine acetylation and methylation are central to the epigenetic regulation of chromatin remodeling. From the early discovery of histone deacetylase inhibitors to the more recent identification of histone demethylase blockers, chemical approaches offer increasingly sophisticated tools for the investigation of the structure and function of these lysine-modifying enzymes. This review summarizes progress to date on compounds identified from screens or by design that can modulate the activity of classical histone deacetylases, sirtuins, histone acetyltransferases, histone methyltransferases and histone demethylases. We highlight applications of compounds to mechanistic and functional studies involving these enzymes and discuss future challenges regarding target specificity and general utility.
Figures
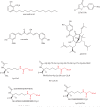
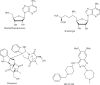
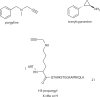
References
-
- Goldberg AD, Allis CD, Bernstein E. Epigenetics: a landscape takes shape. Cell. 2007;128:635–638. - PubMed
-
- Murray K. The occurrence of ε-N-methyl lysine in histones. Biochemistry. 1964;3:10–15. - PubMed
-
- Gershey EL, Vidali G, Allfrey VG. Chemical studies of histone acetylation. The occurrence of ε-N-acetyllysine in the f2a1 histone. J. Biol. Chem. 1968;243:5018–5022. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

