Imaging mass spectrometry technology and application on ganglioside study; visualization of age-dependent accumulation of C20-ganglioside molecular species in the mouse hippocampus
- PMID: 18800170
- PMCID: PMC2532745
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003232
Imaging mass spectrometry technology and application on ganglioside study; visualization of age-dependent accumulation of C20-ganglioside molecular species in the mouse hippocampus
Abstract
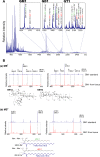
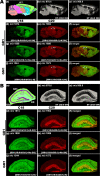
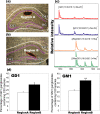
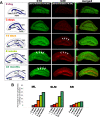
Gangliosides are particularly abundant in the central nervous system (CNS) and thought to play important roles in memory formation, neuritogenesis, synaptic transmission, and other neural functions. Although several molecular species of gangliosides have been characterized and their individual functions elucidated, their differential distribution in the CNS are not well understood. In particular, whether the different molecular species show different distribution patterns in the brain remains unclear. We report the distinct and characteristic distributions of ganglioside molecular species, as revealed by imaging mass spectrometry (IMS). This technique can discriminate the molecular species, raised from both oligosaccharide and ceramide structure by determining the difference of the mass-to-charge ratio, and structural analysis by tandem mass spectrometry. Gangliosides in the CNS are characterized by the structure of the long-chain base (LCB) in the ceramide moiety. The LCB of the main ganglioside species has either 18 or 20 carbons (i.e., C18- or C20-sphingosine); we found that these 2 types of gangliosides are differentially distributed in the mouse brain. While the C18-species was widely distributed throughout the frontal brain, the C20-species selectively localized along the entorhinal-hippocampus projections, especially in the molecular layer (ML) of the dentate gyrus (DG). We revealed development- and aging-related accumulation of the C-20 species in the ML-DG. Thus it is possible to consider that this brain-region specific regulation of LCB chain length is particularly important for the distinct function in cells of CNS.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- van Echten G, Sandhoff K. Ganglioside metabolism. Enzymology, Topology, and regulation. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:5341–5344. - PubMed
-
- Rahmann H. Brain gangliosides and memory formation. Behav Brain Res. 1995;66:105–116. - PubMed
-
- Prinetti A, Iwabuchi K, Hakomori S. Glycosphingolipid-enriched signaling domain in mouse neuroblastoma Neuro2a cells. Mechanism of ganglioside-dependent neuritogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:20916–20924. - PubMed
-
- Ramirez OA, Gomez RA, Carrer HF. Gangliosides improve synaptic transmission in dentate gyrus of hippocampal rat slices. Brain Res. 1990;506:291–293. - PubMed
-
- Kotani M, Terashima T, Tai T. Developmental changes of ganglioside expressions in postnatal rat cerebellar cortex. Brain Res. 1995;700:40–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

