Potent dual thymidylate synthase and dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors: classical and nonclassical 2-amino-4-oxo-5-arylthio-substituted-6-methylthieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine antifolates
- PMID: 18800768
- PMCID: PMC3892769
- DOI: 10.1021/jm8006933
Potent dual thymidylate synthase and dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors: classical and nonclassical 2-amino-4-oxo-5-arylthio-substituted-6-methylthieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine antifolates
Abstract
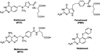
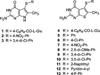
N-{4-[(2-Amino-6-methyl-4-oxo-3,4-dihydrothieno[2,3- d]pyrimidin-5-yl)sulfanyl]benzoyl}-L-glutamic acid (4) and nine nonclassical analogues 5-13 were synthesized as potential dual thymidylate synthase (TS) and dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) inhibitors. The key intermediate in the synthesis was 2-amino-6-methylthieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3 H)-one (16), which was converted to the 5-bromo-substituted compound 17 followed by an Ullmann reaction to afford 5-13. The classical analogue 4 was synthesized by coupling the benzoic acid derivative 19 with diethyl L-glutamate and saponification. Compound 4 is the most potent dual inhibitor of human TS (IC 50 = 40 nM) and human DHFR (IC 50 = 20 nM) known to date. The nonclassical analogues 5- 13 were moderately potent against human TS with IC 50 values ranging from 0.11 to 4.6 microM. The 4-nitrophenyl analogue 7 was the most potent compound in the nonclassical series, demonstrating potent dual inhibitory activities against human TS and DHFR. This study indicated that the 5-substituted 2-amino-4-oxo-6-methylthieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine scaffold is highly conducive to dual human TS-DHFR inhibitory activity.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis, and X-ray crystal structure of classical and nonclassical 2-amino-4-oxo-5-substituted-6-ethylthieno[2,3-d]pyrimidines as dual thymidylate synthase and dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors and as potential antitumor agents.J Med Chem. 2009 Aug 13;52(15):4892-902. doi: 10.1021/jm900490a. J Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19719239 Free PMC article.
-
2,4-Diamino-5-methyl-6-substituted arylthio-furo[2,3-d]pyrimidines as novel classical and nonclassical antifolates as potential dual thymidylate synthase and dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem. 2010 Jan 15;18(2):953-61. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2009.11.029. Epub 2009 Dec 26. Bioorg Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20056546 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of N-{4-[(2,4-diamino-5-methyl-4,7-dihydro-3H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-6-yl)thio]benzoyl}-L-glutamic acid and N-{4-[(2-amino-4-oxo-5-methyl-4,7-dihydro-3H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-6-yl)thio]benzoyl}-L-glutamic acid as dual inhibitors of dihydrofolate reductase and thymidylate synthase and as potential antitumor agents.J Med Chem. 2005 Nov 17;48(23):7215-22. doi: 10.1021/jm058234m. J Med Chem. 2005. PMID: 16279780
-
Nonpolyglutamatable antifolates as inhibitors of thymidylate synthase (TS) and potential antitumour agents.Curr Med Chem. 1998 Aug;5(4):265-88. Curr Med Chem. 1998. PMID: 9668195 Review.
-
Recent advances in classical and non-classical antifolates as antitumor and antiopportunistic infection agents: part I.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2007 Sep;7(5):524-42. doi: 10.2174/187152007781668724. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17896913 Review.
Cited by
-
An innovative strategy for dual inhibitor design and its application in dual inhibition of human thymidylate synthase and dihydrofolate reductase enzymes.PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e60470. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060470. Epub 2013 Apr 5. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23577115 Free PMC article.
-
The Gewald multicomponent reaction.Mol Divers. 2011 Feb;15(1):3-33. doi: 10.1007/s11030-010-9229-6. Epub 2010 Feb 27. Mol Divers. 2011. PMID: 20191319 Review.
-
Design, synthesis, crystal structure and anti-plasmodial evaluation of tetrahydrobenzo[4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives.RSC Med Chem. 2021 May 18;12(6):970-981. doi: 10.1039/d1md00038a. eCollection 2021 Jun 23. RSC Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34223162 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of 5,7-disubstituted-4-methyl-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-2-amines as microtubule inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem. 2013 Mar 1;21(5):1180-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2012.12.029. Epub 2013 Jan 3. Bioorg Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23352482 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis, and X-ray crystal structure of classical and nonclassical 2-amino-4-oxo-5-substituted-6-ethylthieno[2,3-d]pyrimidines as dual thymidylate synthase and dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors and as potential antitumor agents.J Med Chem. 2009 Aug 13;52(15):4892-902. doi: 10.1021/jm900490a. J Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19719239 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chan DCM, Anderson AC. Towards Species-Specific Antifolates. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006;13:377–398. - PubMed
-
- Hawser S, Lociuro S, Islam K. Dihydrofolate Reductase Inhibitors as Antibacterial Agents. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006;71:941–948. - PubMed
-
- Gangjee A, Kurup S, Namjoshi O. Dihydrofolate Reductase as a Target for Chemotherapy in Parasites. Curr. Phartm. Des. 2007;13:609–639. - PubMed
-
- Berman EM, Werbel LM. The Renewed Potential for Folate Antagonists in Contemporary Cancer Chemotherapy. J. Mec. Chem. 1991;34:479–485. - PubMed
-
- Blakley RL. Dihydrofolate Reductase. In: Blakley RL, Benkovic SJ, editors. Folate and Pterins. Vol. I. New York: Wiley-Interscience; 1984. pp. 191–253.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information

