Work-related ill health in general practice, as reported to a UK-wide surveillance scheme
- PMID: 18801281
- PMCID: PMC2529201
- DOI: 10.3399/bjgp08X330753
Work-related ill health in general practice, as reported to a UK-wide surveillance scheme
Abstract
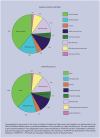
GPs with training in occupational medicine report cases of work-related ill health and sickness absence to The Health and Occupation Reporting network in General Practice (THOR-GP) using an online webform. This report describes the data reported in 2006 and 2007. GPs mainly reported musculoskeletal disorders and mental ill-health. A much larger proportion of the mental ill-health cases were sickness-absence certified, making up 55.9% of the total days certified. Musculoskeletal disorders are the most frequently reported diagnoses of work-related ill health, but mental ill-health is responsible for most work-related sickness absence.
Figures
References
-
- Health and Safety Executive. HSE statistics — key figures for 2006/07. http://www.hse.gov.uk/statistics/index.htm (accessed 21 Jul 2008)
-
- Black C. Working for a healthier tomorrow — Dame Carol Black's review of the health of the working age population. London: TSO; 2008.
-
- University of Manchester. The Health and Occupation Reporting Network (THOR) http://www.medicine.manchester.ac.uk/coeh/thor/ (accessed 21 Jul 2008)
-
- Meyer JD, Chen Y, Holt DL, et al. Occupational contact dermatitis in the UK: a surveillance report from EPIDERM and OPRA. Occup Med (Lond) 2000;50(4):265–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical