Common SNPs in HMGCR in micronesians and whites associated with LDL-cholesterol levels affect alternative splicing of exon13
- PMID: 18802019
- PMCID: PMC2764366
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.108.172288
Common SNPs in HMGCR in micronesians and whites associated with LDL-cholesterol levels affect alternative splicing of exon13
Abstract
Background- Variation in LDL-cholesterol (LDL-C) among individuals is a complex genetic trait involving multiple genes and gene-environment interactions.
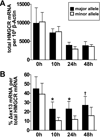
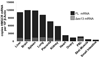
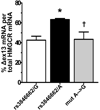
Methods and results: In a genome-wide association study (GWAS) to identify genetic variants influencing LDL-C in an isolated population from Kosrae, we observed associations for SNPs in the gene encoding 3hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl (HMG)-coenzyme A (CoA) reductase (HMGCR). Three of these SNPs (rs7703051, rs12654264, and rs3846663) met the statistical threshold of genome-wide significance when combined with data from the Diabetes Genetics Initiative GWAS. We followed up the association results and identified a functional SNP in intron13 (rs3846662), which was in linkage disequilibrium with the SNPs of genome-wide significance and affected alternative splicing of HMGCR mRNA. In vitro studies in human lymphoblastoid cells demonstrated that homozygosity for the rs3846662 minor allele was associated with up to 2.2-fold lower expression of alternatively spliced HMGCR mRNA lacking exon13, and minigene transfection assays confirmed that allele status at rs3846662 directly modulated alternative splicing of HMGCR exon13 (42.9+/-3.9 versus 63.7+/-1.0%Deltaexon13/total HMGCR mRNA, P=0.02). Further, the alternative splice variant could not restore HMGCR activity when expressed in HMGCR deficient UT-2 cells.
Conclusions: We identified variants in HMGCR that are associated with LDL-C across populations and affect alternative splicing of HMGCR exon13.
Figures
References
-
- Kuulasmaa K, Tunstall-Pedoe H, Dobson A, Fortmann S, Sans S, Tolonen H, Evans A, Ferrario M, Tuomilehto J. Estimation of contribution of changes in classic risk factors to trends in coronary-event rates across the WHO MONICA Project populations. Lancet. 2000;355:675–687. - PubMed
-
- Heller DA, de Faire U, Pedersen NL, Dahlen G, McClearn GE. Genetic and environmental influences on serum lipid levels in twins. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1150–1156. - PubMed
-
- Breslow JL. Genetics of lipoprotein abnormalities associated with coronary artery disease susceptibility. Annu Rev Genet. 2000;34:233–254. - PubMed
-
- Han Z, Heath SC, Shmulewitz D, Li W, Auerbach SB, Blundell ML, Lehner T, Ott J, Stoffel M, Friedman JM, Breslow JL. Candidate genes involved in cardiovascular risk factors by a family-based association study on the island of Kosrae, Federated States of Micronesia. Am J Med Genet. 2002;110:234–242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

