Induction of IL-17+ T cell trafficking and development by IFN-gamma: mechanism and pathological relevance in psoriasis
- PMID: 18802076
- PMCID: PMC2677162
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.7.4733
Induction of IL-17+ T cell trafficking and development by IFN-gamma: mechanism and pathological relevance in psoriasis
Abstract
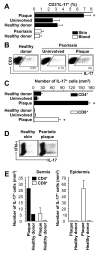
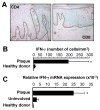
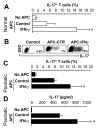
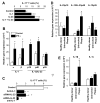
Th1 and Th17 T cells are often colocalized in pathological environments, yet Th1-derived IFN-gamma inhibits Th17 cell development in vitro. We explored the physiologic basis of this paradox in humans. In this study, we demonstrate increased the number of CD4(+) and CD8(+) IL-17(+) T cells in skin lesions of psoriasis. Furthermore, we show that myeloid APCs potently support induction of IL-17(+) T cells, and that this activity is greatly increased in psoriasis. We tested stimuli that might account for this activity. Th1 cells and IFN-gamma are increased in psoriatic blood and lesional skin. We show that IFN-gamma programs myeloid APCs to induce human IL-17(+) T cells via IL-1 and IL-23. IFN-gamma also stimulates APC production of CCL20, supporting migration of IL-17(+) T cells, and synergizes with IL-17 in the production of human beta-defensin 2, an antimicrobial and chemotactic protein highly overexpressed by psoriatic keratinocytes. This study reveals a novel mechanistic interaction between Th1 and IL-17(+) T cells, challenges the view that Th1 cells suppress Th17 development through IFN-gamma, and suggests that Th1 and IL-17(+) T cells may collaboratively contribute to human autoimmune diseases.
Figures


References
-
- Kolls JK, Linden A. Interleukin-17 family members and inflammation. Immunity. 2004;21:467–476. - PubMed
-
- Weaver CT, Harrington LE, Mangan PR, Gavrieli M, Murphy KM. Th17: an effector CD4 T cell lineage with regulatory T cell ties. Immunity. 2006;24:677–688. - PubMed
-
- Dong C. Diversification of T-helper-cell lineages: finding the family root of IL-17-producing cells. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:329–333. - PubMed
-
- Wynn TA. T(H)-17: a giant step from T(H)1 and T(H)2. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:1069–1070. - PubMed
-
- Harrington LE, Hatton RD, Mangan PR, Turner H, Murphy TL, Murphy KM, Weaver CT. Interleukin 17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:1123–1132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

