Distinct regulation of integrin-dependent T cell conjugate formation and NF-kappa B activation by the adapter protein ADAP
- PMID: 18802088
- PMCID: PMC2593878
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.7.4840
Distinct regulation of integrin-dependent T cell conjugate formation and NF-kappa B activation by the adapter protein ADAP
Abstract
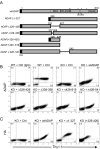
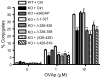
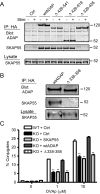
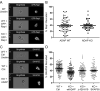
Following TCR stimulation, T cells utilize the hematopoietic specific adhesion and degranulation-promoting adapter protein (ADAP) to control both integrin adhesive function and NF-kappaB transcription factor activation. We have investigated the molecular basis by which ADAP controls these events in primary murine ADAP(-/-) T cells. Naive DO11.10/ADAP(-/-) T cells show impaired adhesion to OVAp (OVA aa 323-339)-bearing APCs that is restored following reconstitution with wild-type ADAP. Mutational analysis demonstrates that the central proline-rich domain and the C-terminal domain of ADAP are required for rescue of T:APC conjugate formation. The ADAP proline-rich domain is sufficient to bind and stabilize the expression of SKAP55 (Src kinase-associated phosphoprotein of 55 kDa), which is otherwise absent from ADAP(-/-) T cells. Interestingly, forced expression of SKAP55 in the absence of ADAP is insufficient to drive T:APC conjugate formation, demonstrating that both ADAP and SKAP55 are required for optimal LFA-1 function. Additionally, the ADAP proline-rich domain is required for optimal Ag-induced activation of CD69, CD25, and Bcl-x(L), but is not required for assembly of the CARMA1/Bcl10/Malt1 (caspase-recruitment domain (CARD) membrane-associated guanylate kinase (MAGUK) protein 1/B-cell CLL-lymphoma 10/mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1) signaling complex and subsequent TCR-dependent NF-kappaB activity. Our results indicate that ADAP is used downstream of TCR engagement to delineate two distinct molecular programs in which the ADAP/SKAP55 module is required for control of T:APC conjugate formation and functions independently of ADAP/CARMA1-mediated NF-kappaB activation.
Figures



References
-
- Simeoni L, Kliche S, Lindquist J, Schraven B. Adaptors and linkers in T and B cells. Curr Opin Immunol. 2004;16:304–313. - PubMed
-
- Samelson LE. Signal transduction mediated the T cell antigen receptor: the role of adapter proteins. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:371–394. - PubMed
-
- Jordan MS, Singer AL, Koretzky GA. Adaptors as central mediators of signal transduction in immune cells. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:110–116. - PubMed
-
- Sommers CL, Samelson LE, Love PE. LAT: a T lymphocyte adapter protein that couples the antigen receptor to downstream signaling pathways. BioEssays. 2004;26:61–67. - PubMed
-
- Zhang WG, Sommers CL, Burshtyn DN, Stebbins CC, DeJarnette JB, Trible RP, Grinberg A, Tsay HC, Jacobs HM, Kessler CM, Long EO, Love PE, Samelson LE. Essential role of LAT in T cell development. Immunity. 1999;10:323–332. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

