IL-17 is a critical component of vaccine-induced protection against lung infection by lipopolysaccharide-heterologous strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 18802100
- PMCID: PMC2597098
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.7.4965
IL-17 is a critical component of vaccine-induced protection against lung infection by lipopolysaccharide-heterologous strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
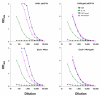
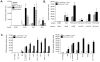
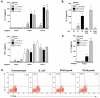
In a murine model of acute fatal pneumonia, we previously showed that nasal immunization with a live-attenuated aroA deletant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO1 elicited LPS serogroup-specific protection, indicating that opsonic Ab to the LPS O Ag was the most important immune effector. Because P. aeruginosa strain PA14 possesses additional virulence factors, we hypothesized that a live-attenuated vaccine based on PA14 might elicit a broader array of immune effectors. Thus, an aroA deletant of PA14, denoted PA14DeltaaroA, was constructed. PA14DeltaaroA-immunized mice were protected against lethal pneumonia caused not only by the parental strain but also by cytotoxic variants of the O Ag-heterologous P. aeruginosa strains PAO1 and PAO6a,d. Remarkably, serum from PA14DeltaaroA-immunized mice had very low levels of opsonic activity against strain PAO1 and could not passively transfer protection, suggesting that an antibody-independent mechanism was needed for the observed cross-serogroup protection. Compared with control mice, PA14DeltaaroA-immunized mice had more rapid recruitment of neutrophils to the airways early after challenge. T cells isolated from P. aeruginosa DeltaaroA-immunized mice proliferated and produced IL-17 in high quantities after coculture with gentamicin-killed P. aeruginosa. Six hours following challenge, PA14DeltaaroA-immunized mice had significantly higher levels of IL-17 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid compared with unimmunized, Escherichia coli-immunized, or PAO1DeltaaroA-immunized mice. Antibody-mediated depletion of IL-17 before challenge or absence of the IL-17 receptor abrogated the PA14DeltaaroA vaccine's protection against lethal pneumonia. These data show that IL-17 plays a critical role in antibody-independent vaccine-induced protection against LPS-heterologous strains of P. aeruginosa in the lung.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mucosal vaccination with a multivalent, live-attenuated vaccine induces multifactorial immunity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa acute lung infection.Infect Immun. 2011 Mar;79(3):1289-99. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01139-10. Epub 2010 Dec 13. Infect Immun. 2011. PMID: 21149583 Free PMC article.
-
Protection against fatal Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia in mice after nasal immunization with a live, attenuated aroA deletion mutant.Infect Immun. 2003 Mar;71(3):1453-61. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.3.1453-1461.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 12595463 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a Protective Vaccine Against Lipopolysaccharide-Heterologous Pseudomonas aeruginosa Strains Based on Expression Profiling of Outer Membrane Proteins During Infection.Front Immunol. 2018 Jul 26;9:1737. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01737. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30093906 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa antigens as potential vaccines.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1997 Nov;21(3):243-77. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.1997.tb00353.x. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1997. PMID: 9451816 Review.
-
Vaccination promotes TH1-like inflammation and survival in chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia. A new prophylactic principle.Behring Inst Mitt. 1997 Feb;(98):269-73. Behring Inst Mitt. 1997. PMID: 9382750 Review.
Cited by
-
IL-17 mediates protective immunity against nasal infection with Bordetella pertussis by mobilizing neutrophils, especially Siglec-F+ neutrophils.Mucosal Immunol. 2021 Sep;14(5):1183-1202. doi: 10.1038/s41385-021-00407-5. Epub 2021 May 11. Mucosal Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33976385 Free PMC article.
-
The role of interleukin-17 in tumor development and progression.J Exp Med. 2020 Jan 6;217(1):e20190297. doi: 10.1084/jem.20190297. J Exp Med. 2020. PMID: 31727782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PvrA is a novel regulator that contributes to Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenesis by controlling bacterial utilization of long chain fatty acids.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jun 19;48(11):5967-5985. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa377. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32406921 Free PMC article.
-
Mucosal vaccination with a multivalent, live-attenuated vaccine induces multifactorial immunity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa acute lung infection.Infect Immun. 2011 Mar;79(3):1289-99. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01139-10. Epub 2010 Dec 13. Infect Immun. 2011. PMID: 21149583 Free PMC article.
-
Collaboration between macrophages and vaccine-induced CD4+ T cells confers protection against lethal Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia during neutropenia.J Infect Dis. 2013 Jan 1;207(1):39-49. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jis657. Epub 2012 Oct 24. J Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23100569 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Safdar N, Dezfulian C, Collard HR, Saint S. Clinical and economic consequences of ventilator-associated pneumonia: a systematic review. Crit. Care Med. 2005;33:2184–2193. - PubMed
-
- Rello J, Rue M, Jubert P, Muses G, Sonora R, Valles J, Niederman MS. Survival in patients with nosocomial pneumonia: impact of the severity of illness and the etiologic agent. Crit. Care Med. 1997;25:1862–1867. - PubMed
-
- Burns JL, Gibson RL, McNamara S, Yim D, Emerson J, Rosenfeld M, Hiatt P, McCoy K, Castile R, Smith AL, Ramsey BW. Longitudinal assessment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in young children with cystic fibrosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2001;183:444–452. - PubMed
-
- Donta ST, Peduzzi P, Cross AS, Sadoff J, Haakenson C, Cryz SJ, Jr., Kauffman C, Bradley S, Gafford G, Elliston D, Beam TR, Jr., John JF, Jr., Ribner B, Cantey R, Welsh CH, Ellison RT, 3rd, Young EJ, Hamill RJ, Leaf H, Schein RM, Mulligan M, Johnson C, Abrutyn E, Griffiss JM, Slagle D, T. F. H. I. T. S. Group Immunoprophylaxis against Klebsiella and Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. The Federal Hyperimmune Immunoglobulin Trial Study Group. J. Infect. Dis. 1996;174:537–543. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

