Cathelicidin administration protects mice from Bacillus anthracis spore challenge
- PMID: 18802102
- PMCID: PMC4225133
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.7.4989
Cathelicidin administration protects mice from Bacillus anthracis spore challenge
Abstract
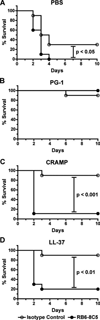
Cathelicidins are a family of cationic peptides expressed in mammals that possess numerous bactericidal and immunomodulatory properties. In vitro analyses showed that human, mouse, and pig cathelicidins inhibited Bacillus anthracis bacterial growth at micromolar concentrations in the presence or absence of capsule. Combined in vitro analyses of the effects of each peptide on spore germination and vegetative outgrowth by time lapse phase contrast microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and flow cytometric analysis showed that only the pig cathelicidin was capable of directly arresting vegetative outgrowth and killing the developing bacilli within the confines of the exosporium. C57BL/6 mice were protected from spore-induced death by each cathelicidin in a time- and dose-dependent manner. Protection afforded by the porcine cathelicidin was due to its bactericidal effects, whereas the human and mouse cathelicidins appeared to mediate protection through increased recruitment of neutrophils to the site of infection. These findings suggest that cathelicidins might be utilized to augment the initial innate immune response to B. anthracis spore exposure and prevent the development of anthrax.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Ganz T. Defensins: antimicrobial peptides of innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003;3:710–720. - PubMed
-
- Yang D, Chertov O, Oppenheim JJ. Participation of mammalian defensins and cathelicidins in anti-microbial immunity: receptors and activities of human defensins and cathelicidin (LL-37) J. Leukocyte Biol. 2001;69:691–697. - PubMed
-
- Finlay BB, Hancock RE. Can innate immunity be enhanced to treat microbial infections? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004;2:497–504. - PubMed
-
- Hancock RE, Diamond G. The role of cationic antimicrobial peptides in innate host defenses. Trends Microbiol. 2000;8:402–410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

