Speedy/Ringo C regulates S and G2 phase progression in human cells
- PMID: 18802405
- PMCID: PMC2592538
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.7.19.6736
Speedy/Ringo C regulates S and G2 phase progression in human cells
Abstract
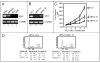
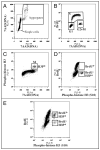
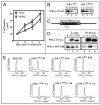
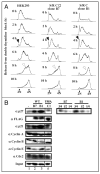
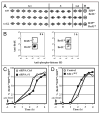
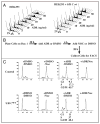
Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) control cell cycle transitions and progression. In addition to their activation via binding to cyclins, CDKs can be activated via binding to an unrelated class of cell cycle regulators termed Speedy/Ringo (S/R) proteins. Although mammals contain at least five distinct Speedy/Ringo homologues, the specific functions of members of this growing family of CDK activators remain largely unknown. We investigated the cell cycle roles of human Speedy/Ringo C in HEK293 cells. Down-regulation of Speedy/Ringo C by RNA interference delayed S and G(2) progression whereas ectopic expression had the opposite effect, reducing S and G(2)/M populations. Double thymidine arrest and release experiments showed that overexpression of Speedy/Ringo C promoted late S phase progression. Using a novel three-color FACS protocol to determine the length of G(2) phase, we found that the suppression of Speedy/Ringo C by RNAi prolonged G(2) phase by approximately 30 min whereas ectopic expression of Speedy/Ringo C shortened G(2) phase by approximately 25 min. In addition, overexpression of Speedy/Ringo C disrupted the G(2) DNA damage checkpoint, increased cell death and caused a cell cycle delay at the G(1)-to-S transition. These observations indicate that CDK-Speedy/Ringo C complexes positively regulate cell cycle progression during the late S and G(2) phases of the cell cycle.
Figures


References
-
- Sherr CJ, Roberts JM. Inhibitors of mammalian G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Genes Dev. 1995;9:1149–63. - PubMed
-
- Sherr CJ, Roberts JM. CDK inhibitors: positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes Dev. 1999;13:1501–12. - PubMed
-
- King RW, Deshaies RJ, Peters JM, Kirschner MW. How proteolysis drives the cell cycle. Science. 1996;274:1652–9. - PubMed
-
- Morgan DO. The dynamics of cyclin dependent kinase structure. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996;8:767–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
