Novel epitope begets a novel pathway in type 1 diabetes progression
- PMID: 18802485
- PMCID: PMC2542855
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI37125
Novel epitope begets a novel pathway in type 1 diabetes progression
Abstract
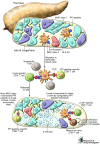
While CD8+ T cells are critical to diabetogenesis in NOD mice, evidence of their involvement in human type 1 diabetes (T1D) has been circumstantial. The existence of CD8+ T cells specific for beta cell peptides has been demonstrated, but functional data regarding the role of these cells in T1D have been lacking. In this issue of the JCI, Skowera et al. describe an unusual self-peptide epitope derived from the leader sequence of preproinsulin (PPI) and show that 50% of HLA-A2+ patients with new-onset T1D possessed circulating CD8+ T cells specific for this epitope, suggesting that PPI plays a critical role in the development of T1D (see the related article beginning on page 3390). They also report that beta cells upregulate PPI expression in the presence of high glucose levels, rendering these cells more susceptible to lysis and potentially accelerating disease. This suggests that interventions aimed at decreasing the PPI-specific CD8+ T cell response early after T1D diagnosis may be efficacious in ameliorating the disease process.
Figures
Comment on
-
CTLs are targeted to kill beta cells in patients with type 1 diabetes through recognition of a glucose-regulated preproinsulin epitope.J Clin Invest. 2008 Oct;118(10):3390-402. doi: 10.1172/JCI35449. J Clin Invest. 2008. PMID: 18802479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wicker L.S., et al. Type 1 diabetes genes and pathways shared by humans and NOD mice. . J. Autoimmun. 2005;25(Suppl.):29–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

