Structure of the S100A6 complex with a fragment from the C-terminal domain of Siah-1 interacting protein: a novel mode for S100 protein target recognition
- PMID: 18803400
- PMCID: PMC2666074
- DOI: 10.1021/bi801233z
Structure of the S100A6 complex with a fragment from the C-terminal domain of Siah-1 interacting protein: a novel mode for S100 protein target recognition
Abstract
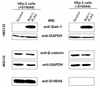
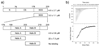
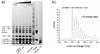
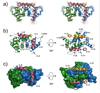
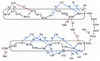
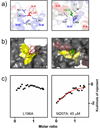
S100A6 is a member of the S100 subfamily of EF-hand Ca (2+) binding proteins that has been shown to interact with calcyclin binding protein/Siah-1 interacting protein (CacyBP/SIP or SIP), a subunit of an SCF-like E3 ubiquitin ligase complex (SCF-TBL1) formed under genotoxic stress. SIP serves as a scaffold in this complex, linking the E2-recruiting module Siah-1 to the substrate-recruiting module Skp1-TBL1. A cell-based functional assay suggests that S100A6 modulates the activity of SCF-TBL1. The results from the cell-based experiments could be enhanced if it were possible to selectively inhibit S100A6-SIP interactions without perturbing any other functions of the two proteins. To this end, the structure of the S100A6-SIP complex was determined in solution by NMR and the strength of the interaction was characterized by isothermal titration calorimetry. In an initial step, the minimal S100A6 binding region in SIP was mapped to a 31-residue fragment (Ser189-Arg219) in the C-terminal domain. The structure of the S100A6-SIP(189-219) complex revealed that SIP(189-219) forms two helices, the first of which (Met193-Tyr200) interacts with S100A6 in a canonical binding mode. The second helix (Met207-Val216) lies over the S100A6 dimer interface, a mode of binding to S100A6 that has not previously been observed for any target bound to an S100 protein. A series of structure-based SIP mutations showed reduced S100A6 binding affinity, setting the stage for direct functional analysis of S100A6-SIP interactions.
Figures


Similar articles
-
S100A6 protein negatively regulates CacyBP/SIP-mediated inhibition of gastric cancer cell proliferation and tumorigenesis.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30185. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030185. Epub 2012 Jan 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22295074 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-regulated interaction of Sgt1 with S100A6 (calcyclin) and other S100 proteins.J Biol Chem. 2003 Jul 18;278(29):26923-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211518200. Epub 2003 May 13. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12746458
-
CacyBP/SIP, a calcyclin and Siah-1-interacting protein, binds EF-hand proteins of the S100 family.J Biol Chem. 2002 Aug 9;277(32):28848-52. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M203602200. Epub 2002 May 31. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12042313
-
S100A6 binding protein and Siah-1 interacting protein (CacyBP/SIP): spotlight on properties and cellular function.Amino Acids. 2011 Oct;41(4):773-80. doi: 10.1007/s00726-010-0498-2. Epub 2010 Feb 25. Amino Acids. 2011. PMID: 20182755 Review.
-
Current view on cellular function of S100A6 and its ligands, CacyBP/SIP and Sgt1.Postepy Biochem. 2018 Oct 25;64(3):242-252. doi: 10.18388/pb.2018_136. Postepy Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30656909 Review. English.
Cited by
-
S100A6 protein negatively regulates CacyBP/SIP-mediated inhibition of gastric cancer cell proliferation and tumorigenesis.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30185. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030185. Epub 2012 Jan 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22295074 Free PMC article.
-
Design of high-affinity S100-target hybrid proteins.Protein Sci. 2009 Dec;18(12):2528-36. doi: 10.1002/pro.267. Protein Sci. 2009. PMID: 19827097 Free PMC article.
-
Two functional S100A4 monomers are necessary for regulating nonmuscle myosin-IIA and HCT116 cell invasion.Biochemistry. 2011 Aug 16;50(32):6920-32. doi: 10.1021/bi200498q. Epub 2011 Jul 13. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21721535 Free PMC article.
-
Studying the Structures of Relaxed and Fuzzy Interactions: The Diverse World of S100 Complexes.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Oct 11;8:749052. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.749052. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34708078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The S100A10-annexin A2 complex provides a novel asymmetric platform for membrane repair.J Biol Chem. 2011 Nov 18;286(46):40174-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.244038. Epub 2011 Sep 26. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21949189 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Donato R. Intracellular and extracellular roles of s100 proteins. Microsc. Res. Techniq. 2003;60:540–551. - PubMed
-
- Nelson MR, Chazin WJ. Structures of EF-hand Ca(2+)-binding proteins: diversity in the organization, packing and response to Ca2+ binding. Biometals. 1998;11:297–318. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharya S, Bunick CG, Chazin WJ. Target selectivity in EF-hand calcium binding proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2004;1742:69–79. - PubMed
-
- Chazin WJ. The impact of X-ray crystallography and NMR on intracellular calcium signal transduction by EF-hand proteins: crossing the threshold from structure to biology and medicine. Sci. STKE. 2007;2007:pe27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 ES000267/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009582/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA68485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM75156/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA09582/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 2 P04A 01030/PHS HHS/United States
- R01 GM62112/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM075156/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM58008/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM058008/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 TW006005/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM062112/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 ES00267/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

