Evolution of an insect-specific GROUCHO-interaction motif in the ENGRAILED selector protein
- PMID: 18803772
- PMCID: PMC2597661
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1525-142X.2008.00269.x
Evolution of an insect-specific GROUCHO-interaction motif in the ENGRAILED selector protein
Abstract
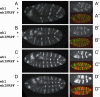
Animal morphology evolves through alterations in the genetic regulatory networks that control development. Regulatory connections are commonly added, subtracted, or modified via mutations in cis-regulatory elements, but several cases are also known where transcription factors have gained or lost activity-modulating peptide motifs. In order to better assess the role of novel transcription factor peptide motifs in evolution, we searched for synapomorphic motifs in the homeotic selectors of Drosophila melanogaster and related insects. Here, we describe an evolutionarily novel GROUCHO (GRO)-interaction motif in the ENGRAILED (EN) selector protein. This "ehIFRPF" motif is not homologous to the previously characterized "engrailed homology 1" (eh1) GRO-interaction motif of EN. This second motif is an insect-specific "WRPW"-type motif that has been maintained by purifying selection in at least the dipteran/lepidopteran lineage. We demonstrate that this motif contributes to in vivo repression of the wingless (wg) target gene and to interaction with GRO in vitro. The acquisition and conservation of this auxiliary peptide motif shows how the number and activity of short peptide motifs can evolve in transcription factors while existing regulatory functions are maintained.
Figures

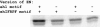
References
-
- Aasland R, Abrams C, Ampe C, Ball LJ, Bedford MT, Cesareni G, Gimona M, Hurley JH, Jarchau T, Lehto VP, et al. Normalization of nomenclature for peptide motifs as ligands of modular protein domains. FEBS Lett. 2002;513:141–4. - PubMed
-
- Adams MD, Celniker SE, Holt RA, Evans CA, Gocayne JD, Amanatides PG, Scherer SE, Li PW, Hoskins RA, Galle RF, et al. The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 2000;287:2185–95. - PubMed
-
- Alonso CR, Maxton-Kuechenmeister J, Akam M. Evolution of Ftz protein function in insects. Curr Biol. 2001;11:1473–8. - PubMed
-
- Brand AH, Perrimon N. Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development. 1993;118:401–15. - PubMed
-
- Brook WJ, Cohen SM. Antagonistic interactions between wingless and decapentaplegic responsible for dorsal-ventral pattern in the Drosophila Leg. Science. 1996;273:1373–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

