Cingulate NMDA NR2B receptors contribute to morphine-induced analgesic tolerance
- PMID: 18803856
- PMCID: PMC2546399
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-6606-1-2
Cingulate NMDA NR2B receptors contribute to morphine-induced analgesic tolerance
Abstract
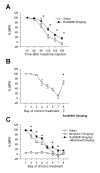
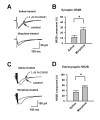
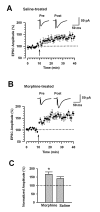
Morphine is widely used to treat chronic pain, however its utility is hindered by the development of tolerance to its analgesic effects. While N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors are known to play roles in morphine tolerance and dependence, less is known about the roles of individual NMDA receptor subtypes. In this study, Ro 256981, an antagonist of the NMDA receptor subunit NR2B, was used to reduce the expression of analgesic tolerance to morphine. The mechanisms altered with chronic drug use share similarities with those underlying the establishment of long-tem potentiation (LTP) and behavioral memory. Since NMDA NR2B receptors in the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) play roles in the establishment of LTP and fear memory, we explored their role in changes that occur in this region after chronic morphine. Both systemic and intra-ACC inhibition of NR2B in morphine-tolerant animals inhibited the expression of analgesic tolerance. Electrophysiological recordings revealed a significant increase in the NR2B component of NMDA receptor mediated excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs), at both synaptic and extra-synaptic sites. However, there was no change in alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptor mediated EPSCs. This study suggests that selective inhibition of NMDA NR2B receptors may prove useful in combating the development of analgesic tolerance to morphine and proposes a novel role for the ACC in opioid tolerance and morphine induced changes in synaptic plasticity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Long-term potentiation in the nucleus accumbens requires both NR2A- and NR2B-containing N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors.Eur J Neurosci. 2008 Apr;27(8):1957-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06173.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18412616
-
Pharmacological isolation of postsynaptic currents mediated by NR2A- and NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in the anterior cingulate cortex.Mol Pain. 2007 Apr 30;3:11. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-3-11. Mol Pain. 2007. PMID: 17470281 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of the C-terminal domain of the NR2B subunit alters channel properties and synaptic targeting of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in nascent neocortical synapses.J Neurosci Res. 2002 May 1;68(3):265-75. doi: 10.1002/jnr.10219. J Neurosci Res. 2002. PMID: 12111856
-
The plasticity of the association between mu-opioid receptor and glutamate ionotropic receptor N in opioid analgesic tolerance and neuropathic pain.Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Sep 15;716(1-3):94-105. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.01.066. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23499699 Review.
-
Long-term plasticity of NMDA GluN2B (NR2B) receptor in anterior cingulate cortical synapses.Mol Pain. 2024 Jan-Dec;20:17448069241230258. doi: 10.1177/17448069241230258. Mol Pain. 2024. PMID: 38246915 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The mitochondrial calcium uniporter contributes to morphine tolerance through pCREB and CPEB1 in rat spinal cord dorsal horn.Br J Anaesth. 2019 Aug;123(2):e226-e238. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2019.05.027. Epub 2019 Jun 26. Br J Anaesth. 2019. PMID: 31253357 Free PMC article.
-
Methadone Reverses Analgesic Tolerance Induced by Morphine Pretreatment.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016 Jun 29;19(7):pyv108. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyv108. Print 2016 Jul. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26390873 Free PMC article.
-
Morphine modulation of pain processing in medial and lateral pain pathways.Mol Pain. 2009 Oct 13;5:60. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-5-60. Mol Pain. 2009. PMID: 19822022 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the NMDA receptor subunit NR2B for the treatment of neuropathic pain.Neurotherapeutics. 2009 Oct;6(4):693-702. doi: 10.1016/j.nurt.2009.07.008. Neurotherapeutics. 2009. PMID: 19789073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Conantokin Peptide Con-T[M8Q] Inhibits Morphine Dependence with High Potency and Low Side Effects.Mar Drugs. 2021 Jan 19;19(1):44. doi: 10.3390/md19010044. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33478061 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

