Plasma carboxyl ester lipase activity modulates apolipoprotein B-containing lipoprotein metabolism in a transgenic mouse model
- PMID: 18803939
- PMCID: PMC2587065
- DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2008.05.003
Plasma carboxyl ester lipase activity modulates apolipoprotein B-containing lipoprotein metabolism in a transgenic mouse model
Abstract
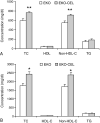
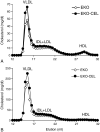
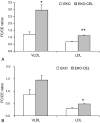
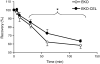
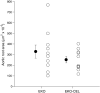
Pancreatic carboxyl ester lipase (CEL) is in the plasma of many mammals, including humans and rats, but not mice. In vitro, CEL hydrolyzes cholesterol esters of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins (apo B-Lp). To study the effect of CEL on metabolism of apo B-Lp and atherosclerosis in vivo, apo E-knockout (EKO) mice, which have high plasma levels of apo B-Lp and are prone to atherosclerosis, were made to secrete CEL into plasma by introducing a transgene containing a liver-specific promoter and rat CEL complementary DNA. Plasma CEL activity in EKO-CEL mice was comparable with that found in rats. Evidence of modification of apo B-Lp by plasma CEL in vivo was an increase in the free cholesterol to cholesterol ester ratio of apo B-Lp from mice on chow or a Western-type diet. In addition, plasma total cholesterol levels were elevated in EKO-CEL mice, with the elevation found exclusively in the apo B-Lp fraction. Associated with the increase in steady-state apo B-Lp levels was an increase in the plasma half-life of very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL) in EKO-CEL mice, measured by the clearance rate of injected VLDL. Interestingly, despite the increase of apo B-Lp, the atherosclerotic lesion did not differ between EKO and EKO-CEL mice on a Western-type diet. In summary, our results demonstrate that plasma CEL modulates apo B-Lp metabolism in vivo, resulting in reduced VLDL clearance and elevated plasma cholesterol levels.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An apolipoprotein(a) peptide delays chylomicron remnant clearance and increases plasma remnant lipoproteins and atherosclerosis in vivo.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005 Aug;25(8):1704-10. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000170819.57945.03. Epub 2005 May 19. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005. PMID: 15905467
-
Apolipoprotein B metabolism in subjects with deficiency of apolipoproteins CIII and AI. Evidence that apolipoprotein CIII inhibits catabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins by lipoprotein lipase in vivo.J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1287-95. doi: 10.1172/JCI112713. J Clin Invest. 1986. PMID: 3095375 Free PMC article.
-
An increased number of very-low-density lipoprotein particles is strongly associated with coronary heart disease in Japanese men, independently of intermediate-density lipoprotein or low-density lipoprotein.Coron Artery Dis. 2002 Aug;13(5):255-62. doi: 10.1097/00019501-200208000-00002. Coron Artery Dis. 2002. PMID: 12394649
-
[Physiology and pathophysiology of the metabolism of lipoproteins].Wien Med Wochenschr. 1994;144(12-13):286-90. Wien Med Wochenschr. 1994. PMID: 8650930 Review. German.
-
[Lipoprotein Lp(a) and CETP (cholesterol ester transfer protein): contribution of transgenic mice].Bull Acad Natl Med. 1994 Mar;178(3):427-34; discussion 434-6. Bull Acad Natl Med. 1994. PMID: 8076182 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Absence of diabetes and pancreatic exocrine dysfunction in a transgenic model of carboxyl-ester lipase-MODY (maturity-onset diabetes of the young).PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e60229. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060229. Epub 2013 Apr 2. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23565203 Free PMC article.
-
Low-density lipoprotein, its susceptibility to oxidation and the role of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 and carboxyl ester lipase lipases in atherosclerotic plaque formation.Arch Med Sci. 2013 Feb 21;9(1):151-8. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2013.33176. Epub 2013 Feb 10. Arch Med Sci. 2013. PMID: 23515030 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang CS, Hartsuck JA. Bile salt-activated lipase. A multiple function lipolytic enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993;1166:1–19. - PubMed
-
- Blackberg L, Lombardo D, Hernell O, et al. Bile salt-stimulated lipase in human milk and carboxyl ester hydrolase in pancreatic juice: are they identical enzymes? FEBS Lett. 1981;136:284–8. - PubMed
-
- Camulli ED, Linke MJ, Brockman HL, Hui DY. Identity of a cytosolic neutral cholesterol esterase in rat liver with the bile salt stimulated cholesterol esterase in pancreas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989;1005:177–82. - PubMed
-
- Zolfaghari R, Harrison EH, Han JH, et al. Tissue and species differences in bile salt-dependent neutral cholesteryl ester hydrolase activity and gene expression. Arterioscler Thromb. 1992;12:295–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

