Spectroscopic and kinetic studies of Nor1, a cytochrome P450 nitric oxide reductase from the fungal pathogen Histoplasma capsulatum
- PMID: 18804446
- PMCID: PMC2603478
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2008.09.001
Spectroscopic and kinetic studies of Nor1, a cytochrome P450 nitric oxide reductase from the fungal pathogen Histoplasma capsulatum
Abstract
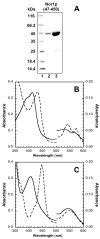
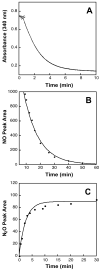
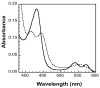
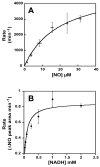
The fungal respiratory pathogen Histoplasma capsulatum evades the innate immune response and colonizes macrophages during infection. Although macrophage production of the antimicrobial effector nitric oxide (NO) restricts H. capsulatum growth, the pathogen is able to establish a persistent infection. H. capsulatum contains a P450 nitric oxide reductase homologue (NOR1) that may be important for detoxifying NO during infection. To characterize the activity of this putative P450 enzyme, a 404 amino acid fragment of Nor1p was expressed in Escherichia coli and purified to homogeneity. Spectral characterization of Nor1p indicated that it was similar to other fungal P450 nitric oxide reductases. Nor1p catalyzed the reduction of NO to N2O using NADH as the direct reductant. The K(M) for NO was determined to be 20 microM and the k(cat) to be 5000 min(-1). Together, these results provide evidence for a protective role of a P450 nitric oxide reductase against macrophage-derived NO.
Figures

References
-
- Marletta MA. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:12231–12234. - PubMed
-
- Moncada S, Palmer RM, Higgs EA. Pharmacol Rev. 1991;43:109–142. - PubMed
-
- Wienberg JB. In: Nitric oxide and infection. Fang FC, editor. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers; New York: 1999. pp. 95–150.
-
- Dedon PC, Tannenbaum SR. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2004;423:12–22. - PubMed
-
- DeGroote MA, Fang FC. In: Nitric oxide and infection. Fang FC, editor. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers; New York: 1999. pp. 231–261.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

