A polymeric protein anchors the chromosomal origin/ParB complex at a bacterial cell pole
- PMID: 18805088
- PMCID: PMC2745220
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.07.015
A polymeric protein anchors the chromosomal origin/ParB complex at a bacterial cell pole
Abstract
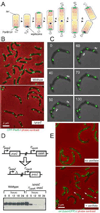
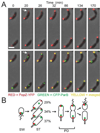
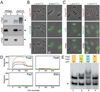
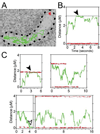
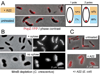
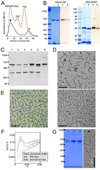
Bacterial replication origins move towards opposite ends of the cell during DNA segregation. We have identified a proline-rich polar protein, PopZ, required to anchor the separated Caulobacter crescentus chromosome origins at the cell poles, a function that is essential for maintaining chromosome organization and normal cell division. PopZ interacts directly with the ParB protein bound to specific DNA sequences near the replication origin. As the origin/ParB complex is being replicated and moved across the cell, PopZ accumulates at the cell pole and tethers the origin in place upon arrival. The polar accumulation of PopZ occurs by a diffusion/capture mechanism that requires the MreB cytoskeleton. High molecular weight oligomers of PopZ assemble in vitro into a filamentous network with trimer junctions, suggesting that the PopZ network and ParB-bound DNA interact in an adhesive complex, fixing the chromosome origin at the cell pole.
Figures
Comment in
-
Grasping at origins.Cell. 2008 Sep 19;134(6):916-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.09.004. Cell. 2008. PMID: 18805084
References
-
- Barak I, Wilkinson AJ. Where asymmetry in gene expression originates. Mol Microbiol. 2005;57:611–620. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Yehuda S, Fujita M, Liu XS, Gorbatyuk B, Skoko D, Yan J, Marko JF, Liu JS, Eichenberger P, Rudner DZ, Losick R. Defining a centromerelike element in Bacillus subtilis by Identifying the binding sites for the chromosome-anchoring protein RacA. Mol Cell. 2005;17:773–782. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Yehuda S, Rudner DZ, Losick R. RacA, a bacterial protein that anchors chromosomes to the cell poles. Science. 2003;299:532–536. - PubMed
-
- Carballido-Lopez R, Formstone A, Li Y, Ehrlich SD, Noirot P, Errington J. Actin homolog MreBH governs cell morphogenesis by localization of the cell wall hydrolase LytE. Dev Cell. 2006;11:399–409. - PubMed
-
- Divakaruni AV, Baida C, White CL, Gober JW. The cell shape proteins MreB and MreC control cell morphogenesis by positioning cell wall synthetic complexes. Mol Microbiol. 2007;66:174–188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

