Intramolecular strain coordinates kinesin stepping behavior along microtubules
- PMID: 18805095
- PMCID: PMC2613771
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.07.018
Intramolecular strain coordinates kinesin stepping behavior along microtubules
Abstract
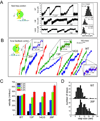
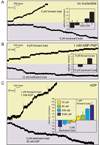
Kinesin advances 8 nm along a microtubule per ATP hydrolyzed, but the mechanism responsible for coordinating the enzymatic cycles of kinesin's two identical motor domains remains unresolved. Here, we have tested whether such coordination is mediated by intramolecular tension generated by the "neck linkers," mechanical elements that span between the motor domains. When tension is reduced by extending the neck linkers with artificial peptides, the coupling between ATP hydrolysis and forward stepping is impaired and motor's velocity decreases as a consequence. However, speed recovers to nearly normal levels when external tension is applied by an optical trap. Remarkably, external load also induces bidirectional stepping of an immotile kinesin that lacks its mechanical element (neck linker) and fuel (ATP). Our results indicate that the kinesin motor domain senses and responds to strain in a manner that facilitates its plus-end-directed stepping and communication between its two motor domains.
Figures





Comment in
-
Kinesin motors: no strain, no gain.Cell. 2008 Sep 19;134(6):918-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.09.005. Cell. 2008. PMID: 18805085
References
-
- Carter NJ, Cross RA. Mechanics of the kinesin step. Nature. 2005;435:308–312. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

