WRN protects against topo I but not topo II inhibitors by preventing DNA break formation
- PMID: 18805512
- PMCID: PMC2606036
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2008.08.008
WRN protects against topo I but not topo II inhibitors by preventing DNA break formation
Abstract
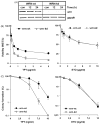
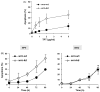
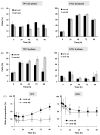
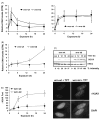
The Werner syndrome helicase/3'-exonuclease (WRN) is a major component of the DNA repair and replication machinery. To analyze whether WRN is involved in the repair of topoisomerase-induced DNA damage we utilized U2-OS cells, in which WRN is stably down-regulated (wrn-kd), and the corresponding wild-type cells (wrn-wt). We show that cells not expressing WRN are hypersensitive to the toxic effect of the topoisomerase I inhibitor topotecan, but not to the topoisomerase II inhibitor etoposide. This was shown by mass survival assays, colony formation and induction of apoptosis. Upon topotecan treatment WRN deficient cells showed enhanced DNA replication inhibition and S-phase arrest, whereas after treatment with etoposide they showed the same cell cycle response as the wild-type. A considerable difference between WRN and wild-type cells was observed for DNA single- and double-strand break formation in response to topotecan. Topotecan induced DNA single-strand breaks 6h after treatment. In both wrn-wt and wrn-kd cells these breaks were repaired at similar kinetics. However, in wrn-kd but not wrn-wt cells they were converted into DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) at high frequency, as shown by neutral comet assay and phosphorylation of H2AX. Our data provide evidence that WRN is involved in the repair of topoisomerase I, but not topoisomerase II-induced DNA damage, most likely via preventing the conversion of DNA single-strand breaks into DSBs during the resolution of stalled replication forks at topo I-DNA complexes. We suggest that the WRN status of tumor cells impacts anticancer therapy with topoisomerase I, but not topoisomerase II inhibitors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of helicase activity by a small molecule impairs Werner syndrome helicase (WRN) function in the cellular response to DNA damage or replication stress.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jan 25;108(4):1525-30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1006423108. Epub 2011 Jan 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21220316 Free PMC article.
-
Topotecan-triggered degradation of topoisomerase I is p53-dependent and impacts cell survival.Cancer Res. 2005 Oct 1;65(19):8920-6. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0266. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16204064
-
Werner's syndrome lymphoblastoid cells are hypersensitive to topoisomerase II inhibitors in the G2 phase of the cell cycle.Mutat Res. 2000 Mar 20;459(2):123-33. doi: 10.1016/s0921-8777(99)00065-8. Mutat Res. 2000. PMID: 10725663
-
Roles of the Werner syndrome RecQ helicase in DNA replication.DNA Repair (Amst). 2008 Nov 1;7(11):1776-86. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2008.07.017. Epub 2008 Sep 6. DNA Repair (Amst). 2008. PMID: 18722555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of WRN in DNA repair is affected by post-translational modifications.Mech Ageing Dev. 2007 Jan;128(1):50-7. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2006.11.010. Epub 2006 Nov 20. Mech Ageing Dev. 2007. PMID: 17116323 Review.
Cited by
-
Human RecQ helicases in DNA repair, recombination, and replication.Annu Rev Biochem. 2014;83:519-52. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-060713-035428. Epub 2014 Mar 3. Annu Rev Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24606147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Copy number changes at 8p11-12 predict adverse clinical outcome and chemo- and radiotherapy response in breast cancer.Oncotarget. 2018 Mar 30;9(24):17078-17092. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24904. eCollection 2018 Mar 30. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29682206 Free PMC article.
-
Association of epigenetic inactivation of the WRN gene with anticancer drug sensitivity in cervical cancer cells.Oncol Rep. 2012 Oct;28(4):1146-52. doi: 10.3892/or.2012.1912. Epub 2012 Jul 13. Oncol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22797812 Free PMC article.
-
RECQL5 plays co-operative and complementary roles with WRN syndrome helicase.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jan;41(2):881-99. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1134. Epub 2012 Nov 23. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23180761 Free PMC article.
-
Non-enzymatic function of WRN RECQL helicase regulates removal of topoisomerase-I-DNA covalent complexes and triggers NF-κB signaling in cancer.Aging Cell. 2022 Jun;21(6):e13625. doi: 10.1111/acel.13625. Epub 2022 May 18. Aging Cell. 2022. PMID: 35582959 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Slichenmyer WJ, Von Hoff DD. New natural products in cancer chemotherapy. J Clin Pharmacol. 1990;30:770–788. - PubMed
-
- Pommier Y. Topoisomerase I inhibitors: camptothecins and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:789–802. - PubMed
-
- Nitiss JL, Wang JC. Mechanisms of cell killing by drugs that trap covalent complexes between DNA topoisomerases and DNA. Mol Pharmacol. 1996;50:1095–1102. - PubMed
-
- Hertzberg RP, Caranfa MJ, Hecht SM. On the mechanism of topoisomerase I inhibition by camptothecin: evidence for binding to an enzyme–DNA complex. Biochemistry. 1989;28:4629–4638. - PubMed
-
- Hsiang YH, Hertzberg R, Hecht S, Liu LF. Camptothecin induces protein-linked DNA breaks via mammalian DNA topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:14873–14878. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

