WRN protects against topo I but not topo II inhibitors by preventing DNA break formation
- PMID: 18805512
- PMCID: PMC2606036
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2008.08.008
WRN protects against topo I but not topo II inhibitors by preventing DNA break formation
Abstract
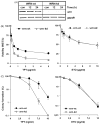
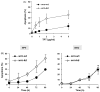
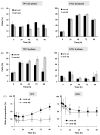
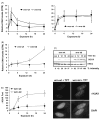
The Werner syndrome helicase/3'-exonuclease (WRN) is a major component of the DNA repair and replication machinery. To analyze whether WRN is involved in the repair of topoisomerase-induced DNA damage we utilized U2-OS cells, in which WRN is stably down-regulated (wrn-kd), and the corresponding wild-type cells (wrn-wt). We show that cells not expressing WRN are hypersensitive to the toxic effect of the topoisomerase I inhibitor topotecan, but not to the topoisomerase II inhibitor etoposide. This was shown by mass survival assays, colony formation and induction of apoptosis. Upon topotecan treatment WRN deficient cells showed enhanced DNA replication inhibition and S-phase arrest, whereas after treatment with etoposide they showed the same cell cycle response as the wild-type. A considerable difference between WRN and wild-type cells was observed for DNA single- and double-strand break formation in response to topotecan. Topotecan induced DNA single-strand breaks 6h after treatment. In both wrn-wt and wrn-kd cells these breaks were repaired at similar kinetics. However, in wrn-kd but not wrn-wt cells they were converted into DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) at high frequency, as shown by neutral comet assay and phosphorylation of H2AX. Our data provide evidence that WRN is involved in the repair of topoisomerase I, but not topoisomerase II-induced DNA damage, most likely via preventing the conversion of DNA single-strand breaks into DSBs during the resolution of stalled replication forks at topo I-DNA complexes. We suggest that the WRN status of tumor cells impacts anticancer therapy with topoisomerase I, but not topoisomerase II inhibitors.
Figures
References
-
- Slichenmyer WJ, Von Hoff DD. New natural products in cancer chemotherapy. J Clin Pharmacol. 1990;30:770–788. - PubMed
-
- Pommier Y. Topoisomerase I inhibitors: camptothecins and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:789–802. - PubMed
-
- Nitiss JL, Wang JC. Mechanisms of cell killing by drugs that trap covalent complexes between DNA topoisomerases and DNA. Mol Pharmacol. 1996;50:1095–1102. - PubMed
-
- Hertzberg RP, Caranfa MJ, Hecht SM. On the mechanism of topoisomerase I inhibition by camptothecin: evidence for binding to an enzyme–DNA complex. Biochemistry. 1989;28:4629–4638. - PubMed
-
- Hsiang YH, Hertzberg R, Hecht S, Liu LF. Camptothecin induces protein-linked DNA breaks via mammalian DNA topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:14873–14878. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

