Human neutrophil peptides: a novel potential mediator of inflammatory cardiovascular diseases
- PMID: 18805897
- PMCID: PMC4896811
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00472.2008
Human neutrophil peptides: a novel potential mediator of inflammatory cardiovascular diseases
Abstract
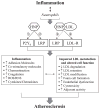
The traditional view of atherosclerosis has recently been expanded from a predominantly lipid retentive disease to a coupling of inflammatory mechanisms and dyslipidemia. Studies have suggested a novel role for polymorphonuclear neutrophil (PMN)-dominant inflammation in the development of atherosclerosis. Human neutrophil peptides (HNPs), also known as alpha-defensins, are secreted and released from PMN granules upon activation and are conventionally involved in microbial killing. Current evidence suggests an important immunomodulative role for these peptides. HNP levels are markedly increased in inflammatory diseases including sepsis and acute coronary syndromes. They have been found within the intima of human atherosclerotic arteries, and their deposition in the skin correlates with the severity of coronary artery diseases. HNPs form complexes with LDL in solution and increase LDL binding to the endothelial surface. HNPs have also been shown to contribute to endothelial dysfunction, lipid metabolism disorder, and the inhibition of fibrinolysis. Given the emerging relationship between PMN-dominant inflammation and atherosclerosis, HNPs may serve as a link between them and as a biological marker and potential therapeutic target in cardiovascular diseases including coronary artery diseases and acute coronary syndromes.
Figures
References
-
- Aarbiou J, Rabe KF, Hiemstra PS. Role of defensins in inflammatory lung disease. Ann Med. 2002;34:96–101. - PubMed
-
- Adams DH, Shaw S. Leucocyte-endothelial interactions and regulation of leucocyte migration. Lancet. 1994;343:831–836. - PubMed
-
- Adrie C, Laurent I, Monchi M, Cariou A, Dhainaou JF, Spaulding C. Postresuscitation disease after cardiac arrest: a sepsis-like syndrome? Curr Opin Crit Care. 2004;10:208–212. - PubMed
-
- Ashitani J, Mukae H, Hiratsuka T, Nakazato M, Kumamoto K, Matsukura S. Elevated levels of alpha-defensins in plasma and BAL fluid of patients with active pulmonary tuberculosis. Chest. 2002;121:519–526. - PubMed
-
- Assmann G, Carmena R, Cullen P, Fruchart JC, Jossa F, Lewis B, Mancini M, Paoletti R. Coronary heart disease: reducing the risk: a worldwide view. International Task Force for the Prevention of Coronary Heart Disease. Circulation. 1999;100:1930–1938. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

