NF-kappaB1 and c-Rel cooperate to promote the survival of TLR4-activated B cells by neutralizing Bim via distinct mechanisms
- PMID: 18805964
- PMCID: PMC3400541
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-10-120832
NF-kappaB1 and c-Rel cooperate to promote the survival of TLR4-activated B cells by neutralizing Bim via distinct mechanisms
Abstract
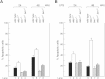
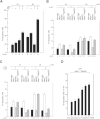
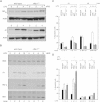
The nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) pathway is crucial for the survival of B cells stimulated through Toll-like receptors (TLRs). Here, we show that the heightened death of TLR4-activated nfkb1(-/-) B cells is the result of a failure of the Tpl(2)/MEK/ERK pathway to phosphorylate the proapo-ptotic BH3-only protein Bim and target it for degradation. ERK inactivation of Bim after TLR4 stimulation is accompanied by an increase in A1/Bim and Bcl-x(L)/Bim complexes that we propose represents a c-Rel-dependent mechanism for neutralizing Bim. Together these findings establish that optimal survival of TLR4-activated B cells depends on the NF-kappaB pathway neutralizing Bim through a combination of Bcl-2 prosurvival protein induction and Tpl2/ERK-dependent Bim phosphorylation and degradation.
Figures




References
-
- Kawai T, Akira S. TLR signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:816–825. - PubMed
-
- Mond JJ, Vos Q, Lees A, Snapper CM. T cell independent antigens. Curr Opin Immunol. 1995;7:349–354. - PubMed
-
- Hayden MS, Ghosh S. Signaling to NF-kappaB. Genes Dev. 2004;18:2195–2224. - PubMed
-
- Karin M, Ben-Neriah Y. Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-[kappa]B activity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000;18:621–663. - PubMed
-
- Grumont RJ, Gerondakis S. The subunit composition of NF-kappa B complexes changes during B-cell development. Cell Growth Differ. 1994;5:1321–1331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

