Genomic predictors of interindividual differences in response to DNA damaging agents
- PMID: 18805990
- PMCID: PMC2559901
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1688508
Genomic predictors of interindividual differences in response to DNA damaging agents
Abstract
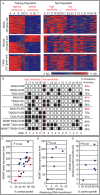
Human lymphoblastoid cells derived from different healthy individuals display considerable variation in their transcription profiles. Here we show that such variation in gene expression underlies interindividual susceptibility to DNA damaging agents. The results demonstrate the massive differences in sensitivity across a diverse cell line panel exposed to an alkylating agent. Computational models identified 48 genes with basal expression that predicts susceptibility with 94% accuracy. Modulating transcript levels for two member genes, MYH and C21ORF56, confirmed that their expression does indeed influence alkylation sensitivity. Many proteins encoded by these genes are interconnected in cellular networks related to human cancer and tumorigenesis.
Figures



References
-
- Begley T.J., Rosenbach A.S., Ideker T., Samson L.D. Hot spots for modulating toxicity identified by genomic phenotyping and localization mapping. Mol. Cell. 2004;16:117–125. - PubMed
-
- Ceccotti S., Aquilina G., Macpherson P., Yamada M., Karran P., Bignami M. Processing of O6-methylguanine by mismatch correction in human cell extracts. Curr. Biol. 1996;6:1528–1531. - PubMed
-
- Cheung V.G., Conlin L.K., Weber T.M., Arcaro M., Jen K.Y., Morley M., Spielman R.S. Natural variation in human gene expression assessed in lymphoblastoid cells. Nat. Genet. 2003;33:422–425. - PubMed
-
- Collins F.S., Brooks L.D., Chakravarti A. A DNA polymorphism discovery resource for research on human genetic variation. Genome Res. 1998;8:1229–1231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
