Multiple protein domains mediate interaction between Bcl10 and MALT1
- PMID: 18806265
- PMCID: PMC2583291
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M800670200
Multiple protein domains mediate interaction between Bcl10 and MALT1
Abstract
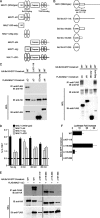
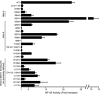
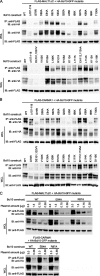
Bcl10 and MALT1 are essential mediators of NF-kappaB activation in response to the triggering of a diverse array of transmembrane receptors, including antigen receptors. Additionally, both proteins are translocation targets in MALT lymphoma. Thus, a detailed understanding of the interaction between these mediators is of considerable biological importance. Previous studies have indicated that a 13-amino acid region downstream of the Bcl10 caspase recruitment domain (CARD) is responsible for interacting with the immunoglobulin-like domains of MALT1. We now provide evidence that the death domain of MALT1 and the CARD of Bcl10 also contribute to Bcl10-MALT1 interactions. Although a direct interaction between the MALT1 death domain and Bcl10 cannot be detected via immunoprecipitation, FRET data strongly suggest that the death domain of MALT1 contributes significantly to the association between Bcl10 and MALT1 in T cells in vivo. Furthermore, analysis of point mutants of conserved residues of Bcl10 shows that the Bcl10 CARD is essential for interaction with the MALT1 N terminus. Mutations that disrupt proper folding of the Bcl10 CARD strongly impair Bcl10-MALT1 interactions. Molecular modeling and functional analyses of Bcl10 point mutants suggest that residues Asp(80) and Glu(84) of helix 5 of the Bcl10 CARD directly contact MALT1. Together, these data demonstrate that the association between Bcl10 and MALT1 involves a complex interaction between multiple protein domains. Moreover, the Bcl10-MALT1 interaction is the second reported example of interactions between a CARD and a non-CARD protein region, which suggests that many signaling cascades may utilize CARD interactions with non-CARD domains.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The protein kinase C-responsive inhibitory domain of CARD11 functions in NF-kappaB activation to regulate the association of multiple signaling cofactors that differentially depend on Bcl10 and MALT1 for association.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Sep;28(18):5668-86. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00418-08. Epub 2008 Jul 14. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18625728 Free PMC article.
-
Psoriasis mutations disrupt CARD14 autoinhibition promoting BCL10-MALT1-dependent NF-κB activation.Biochem J. 2016 Jun 15;473(12):1759-68. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160270. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Biochem J. 2016. PMID: 27071417 Free PMC article.
-
Bcl10 and MALT1, independent targets of chromosomal translocation in malt lymphoma, cooperate in a novel NF-kappa B signaling pathway.J Biol Chem. 2001 Jun 1;276(22):19012-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M009984200. Epub 2001 Mar 21. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11262391
-
Genetic errors of the human caspase recruitment domain-B-cell lymphoma 10-mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma-translocation gene 1 (CBM) complex: Molecular, immunologic, and clinical heterogeneity.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015 Nov;136(5):1139-49. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.06.031. Epub 2015 Aug 12. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26277595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the CARMA1/BCL10/MALT1 complex in lymphoid malignancies.Curr Opin Hematol. 2016 Jul;23(4):402-9. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000257. Curr Opin Hematol. 2016. PMID: 27135977 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ancient Origin of the CARD-Coiled Coil/Bcl10/MALT1-Like Paracaspase Signaling Complex Indicates Unknown Critical Functions.Front Immunol. 2018 May 24;9:1136. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01136. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29881386 Free PMC article.
-
Two Antagonistic MALT1 Auto-Cleavage Mechanisms Reveal a Role for TRAF6 to Unleash MALT1 Activation.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 4;12(1):e0169026. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169026. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28052131 Free PMC article.
-
Malt1 and cIAP2-Malt1 as effectors of NF-kappaB activation: kissing cousins or distant relatives?Cell Signal. 2010 Jan;22(1):9-22. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.09.033. Epub 2009 Sep 19. Cell Signal. 2010. PMID: 19772915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antigen receptor signaling to NF-kappaB via CARMA1, BCL10, and MALT1.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010 Sep;2(9):a003004. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a003004. Epub 2010 Aug 4. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010. PMID: 20685844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of an Ortholog of MALT1 from Shrimp That Induces NF-κB-Mediated Antiviral Immunity.Viruses. 2023 Nov 30;15(12):2361. doi: 10.3390/v15122361. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 38140602 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schulze-Luehrmann, J., and Ghosh, S. (2006) Immunity 25 701–715 - PubMed
-
- Wegener, E., and Krappmann, D. (2007) Science's STKE 2007, pe21 - PubMed
-
- Ruefli-Brasse, A. A., French, D. M., and Dixit, V. M. (2003) Science 302 1581–1584 - PubMed
-
- Ruland, J., Duncan, G. S., Elia, A., del Barco Barrantes, I., Nguyen, L., Plyte, S., Millar, D. G., Bouchard, D., Wakeham, A., Ohashi, P. S., and Mak, T. W. (2001) Cell 104 33–42 - PubMed
-
- Ruland, J., Duncan, G. S., Wakeham, A., and Mak, T. W. (2003) Immunity 19 749–758 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

