Identification of alpha 1L-adrenoceptor in mice and its abolition by alpha 1A-adrenoceptor gene knockout
- PMID: 18806813
- PMCID: PMC2607200
- DOI: 10.1038/bjp.2008.360
Identification of alpha 1L-adrenoceptor in mice and its abolition by alpha 1A-adrenoceptor gene knockout
Abstract
Background and purpose: The alpha(1L)-adrenoceptor has pharmacological properties that distinguish it from three classical alpha(1)-adrenoceptors (alpha(1A), alpha(1B) and alpha(1D)). The purpose of this was to identify alpha(1L)-adrenoceptors in mice and to examine their relationship to classical alpha(1)-adrenoceptors.
Experimental approach: Radioligand binding and functional bioassay experiments were performed on the cerebral cortex, vas deferens and prostate of wild-type (WT) and alpha(1A)-, alpha(1B)- and alpha(1D)-adrenoceptor gene knockout (AKO, BKO and DKO) mice.
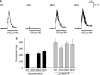
Key results: The radioligand [(3)H]-silodosin bound to intact segments of the cerebral cortex, vas deferens and prostate of WT, BKO and DKO but not of AKO mice. The binding sites were composed of two components with high and low affinities for prazosin or RS-17053, indicating the pharmacological profiles of alpha(1A)-adrenoceptors and alpha(1L)-adrenoceptors. In membrane preparations of WT mouse cortex, however, [(3)H]-silodosin bound to a single population of prazosin high-affinity sites, suggesting the presence of alpha(1A)-adrenoceptors alone. In contrast, [(3)H]-prazosin bound to two components having alpha(1A)-adrenoceptor and alpha(1B)-adrenoceptor profiles in intact segments of WT and DKO mouse cortices, but AKO mice lacked alpha(1A)-adrenoceptor profiles and BKO mice lacked alpha(1B)-adrenoceptor profiles. Noradrenaline produced contractions through alpha(1L)-adrenoceptors with low affinity for prazosin in the vas deferens and prostate of WT, BKO and DKO mice. However, the contractions were abolished or markedly attenuated in AKO mice.
Conclusions and implications: alpha(1L)-Adrenoceptors were identified as binding and functional entities in WT, BKO and DKO mice but not in AKO mice, suggesting that the alpha(1L)-adrenoceptor is one phenotype derived from the alpha(1A)-adrenoceptor gene.
Figures

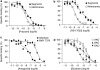



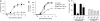
Similar articles
-
RS-17053 (N-[2-(2-cyclopropylmethoxyphenoxy)ethyl]-5-chloro-alpha, alpha-dimethyl-1H-indole-3-ethanamine hydrochloride), a selective alpha 1A-adrenoceptor antagonist, displays low affinity for functional alpha 1-adrenoceptors in human prostate: implications for adrenoceptor classification.Mol Pharmacol. 1996 Feb;49(2):209-15. Mol Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8632751
-
Evaluation of the pharmacological selectivity profile of alpha 1 adrenoceptor antagonists at prostatic alpha 1 adrenoceptors: binding, functional and in vivo studies.Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Jun;118(4):871-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15480.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8799556 Free PMC article.
-
Different subtypes of alpha 1A-adrenoceptor mediating contraction of rat epididymal vas deferens, rat hepatic portal vein and human prostate distinguished by the antagonist RS 17053.Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Sep;119(2):407-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb16001.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8886428 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotype pharmacology of lower urinary tract α(1)-adrenoceptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Mar;165(5):1226-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01591.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21745191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alpha 1-adrenoceptor pharmacome: alpha 1L-adrenoceptor and alpha 1A-adrenoceptor in the lower urinary tract.Int J Urol. 2010 Jan;17(1):31-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2009.02368.x. Epub 2009 Aug 19. Int J Urol. 2010. PMID: 19694838 Review.
Cited by
-
What makes the α(1A)-adrenoceptor gene express the α(1L)-adrenoceptor functional phenotype?Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Mar;165(5):1223-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01663.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21913893 Free PMC article.
-
Agonist pharmacology at recombinant α1A - and α1L -adrenoceptors and in lower urinary tract α1 -adrenoceptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Nov;170(6):1242-52. doi: 10.1111/bph.12403. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24024968 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and pharmacological characterization of AdTx1, a natural peptide displaying specific insurmountable antagonism of the alpha1A-adrenoceptor.Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Jan 1;159(2):316-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00532.x. Epub 2009 Dec 15. Br J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20015090 Free PMC article.
-
What makes the α1A -adrenoceptor gene product assume an α1L -adrenoceptor phenotype?Br J Pharmacol. 2019 Jul;176(14):2358-2365. doi: 10.1111/bph.14599. Epub 2019 Mar 27. Br J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30719698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stimulation of α1a adrenergic receptors induces cellular proliferation or antiproliferative hypertrophy dependent solely on agonist concentration.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 22;8(8):e72430. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072430. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23991110 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amobi N, Guillebaud J, Kaisary A, Lloyd-Davies RW, Turner E, Smith IC. Contractile actions of imidazoline alpha-adrenoceptor agonists and effects of noncompetitive alpha1-adrenoceptor antagonists in human vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 2002;462:169–177. - PubMed
-
- Argyle SA, McGrath JC. An alpha(1A)/alpha(1L)-adrenoceptor mediates contraction of canine subcutaneous resistance arteries. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000;295:627–633. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

